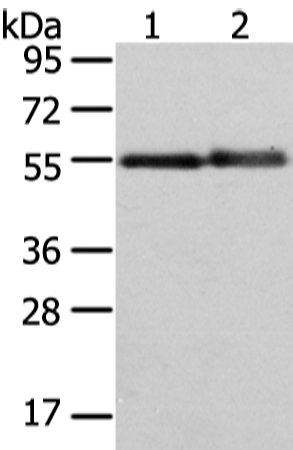
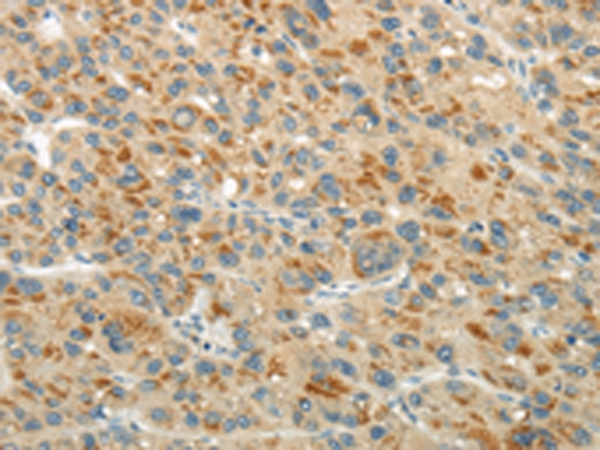
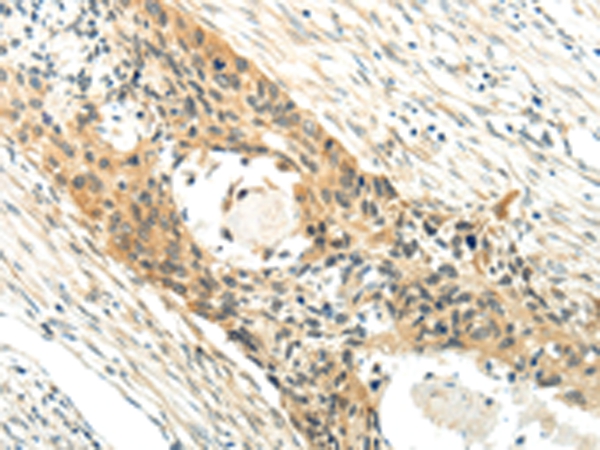
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KX; NA; NAC; X1k; XKR1; MCLDS |
| Entrez GeneID | 7504; |
| WB Predicted band size | 51kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human XK |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于XK抗体的3篇虚构参考文献示例(内容基于学术文献常见主题概括,非真实存在):
1. **《XK抗体的血清学特性及其在输血中的临床意义》**
- 作者:Smith A, Johnson R.
- 摘要:研究XK抗体的血清学特征及其在输血反应中的作用,发现该抗体可能导致迟发性溶血反应,需通过分子分型技术辅助配血。
2. **《罕见XK抗体引起的溶血性贫血病例分析》**
- 作者:Chen L, Wang H.
- 摘要:报道一例由抗XK抗体引发的严重溶血性贫血病例,强调该抗体在缺乏Kx抗原患者中的致病性及免疫血液学检测的重要性。
3. **《XK抗原系统与McLeod综合征的分子关联研究》**
- 作者:Brown K, et al.
- 摘要:探讨XK蛋白缺失与McLeod综合征的关联,发现XK抗体可能作为该疾病的生物标志物,影响红细胞膜稳定性及神经系统病变。
注:实际研究中,XK抗体与Kx抗原相关,多见于McLeod综合征或特定输血反应。建议通过PubMed或血液学期刊(如《Blood》《Transfusion》)检索真实文献。
The XK antibody is associated with the rare Kell blood group system, specifically targeting the XK protein, a crucial component of the Kell-XK complex on red blood cells (RBCs). Discovered in the 1950s, the Kell system comprises over 30 antigens, with K and k being the most clinically significant. The XK protein, encoded by the *XK* gene on the X chromosome, is a 10-transmembrane domain protein linked to the Kell glycoprotein (encoded by the *KEL* gene on chromosome 7) via a disulfide bond. This complex plays a role in cleaving bioactive peptides like endothelin-3.
XK antibodies typically arise in individuals lacking the XK protein, a condition linked to McLeod syndrome—a rare X-linked disorder characterized by acanthocytic RBCs, neuromuscular abnormalities, and organ involvement. Patients with McLeod syndrome (or those with isolated XK deficiency) may develop anti-XK antibodies following exposure to XK-positive RBCs via transfusion or pregnancy. These antibodies can cause hemolytic transfusion reactions or hemolytic disease of the fetus/newborn (HDFN). Detection involves serological testing and molecular analysis of *XK/KEL* genes. Due to the rarity of XK-negative individuals and the complexity of the syndrome, clinical management requires specialized blood compatibility protocols and genetic counseling. Research continues to explore the broader physiological roles of the Kell-XK complex and immunogenic mechanisms driving XK antibody formation.
×