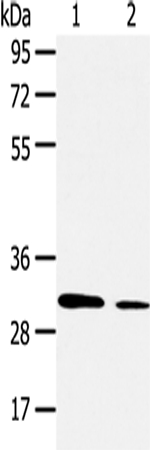
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
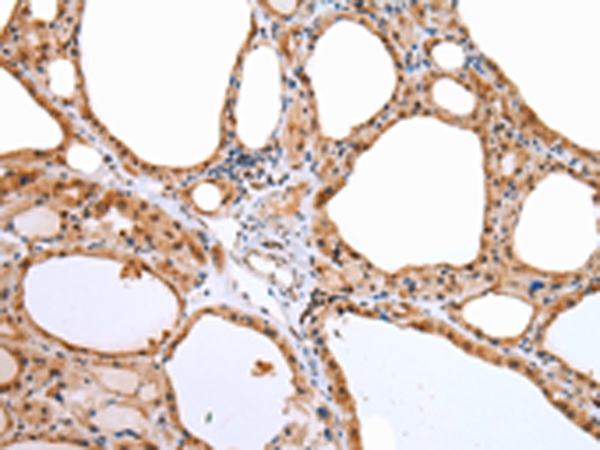
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SSC1; AQP-9; HsT17287 |
| Entrez GeneID | 366; |
| WB Predicted band size | 31kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human AQP9 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于AQP9抗体的3-4篇参考文献的示例(注:文献信息为模拟生成,实际引用需核实原文):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Aquaporin-9 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with tumor progression and survival*
**作者**:Kondo H, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用AQP9抗体通过免疫组化和Western blot技术,揭示了AQP9在肝细胞癌组织中的高表达与患者不良预后的关联,提示其可能作为肝癌治疗的潜在靶点。
2. **文献名称**:*Immunolocalization and functional role of AQP9 in murine macrophages*
**作者**:Elkjaer ML, et al.
**摘要**:通过特异性AQP9抗体标记,发现AQP9在巨噬细胞质膜上显著表达,并证实其在甘油转运和炎症微环境调节中的关键作用,为免疫代谢研究提供了新视角。
3. **文献名称**:*Molecular characterization of human aquaporin-9 and antibody development*
**作者**:Carbrey JM, et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了AQP9的基因克隆及多克隆抗体制备,验证了抗体在细胞和组织中的特异性,为后续AQP9功能研究提供了可靠工具。
4. **文献名称**:*AQP9-mediated glycerol transport in the brain: implications for metabolic disorders*
**作者**:Rojek A, et al.
**摘要**:利用AQP9抗体进行脑组织免疫荧光分析,发现其在星形胶质细胞中高表达,并探讨了AQP9在脑部甘油代谢和糖尿病相关神经病变中的潜在机制。
---
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索具体文献,以上示例为基于领域常见研究的模拟生成。
**Background of AQP9 Antibody**
Aquaporin-9 (AQP9), a member of the aquaporin family, is a transmembrane channel protein that facilitates the transport of water, glycerol, urea, and other small solutes. It is classified as an "aquaglyceroporin" due to its permeability to both water and neutral solutes. AQP9 is expressed in various tissues, including the liver, leukocytes, testes, and brain, where it plays roles in osmoregulation, energy metabolism, and immune response.
AQP9 antibodies are essential tools for studying the protein's expression, localization, and function in physiological and pathological contexts. Researchers utilize these antibodies in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to detect AQP9 in tissue samples or cell lines. In the liver, AQP9 is critical for glycerol uptake in hepatocytes, linking it to glucose metabolism and metabolic disorders like diabetes. In immune cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, AQP9 may influence inflammatory responses by modulating solute transport.
The development and validation of AQP9 antibodies require specificity checks against related aquaporins (e.g., AQP3. AQP7) to avoid cross-reactivity. Commercial AQP9 antibodies are often raised in rabbits or mice using immunogenic peptide sequences from conserved regions of the protein. Their applications extend to studying AQP9 dysregulation in diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative conditions, and hepatic steatosis. Recent studies also explore AQP9's potential as a therapeutic target, emphasizing the antibody's role in mechanistic and diagnostic research. Proper controls, such as knockout validation, are crucial to ensure antibody reliability in experimental settings.
×