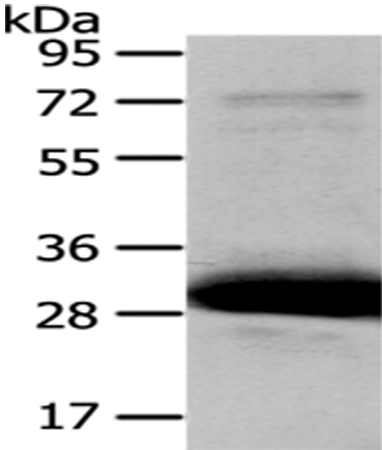
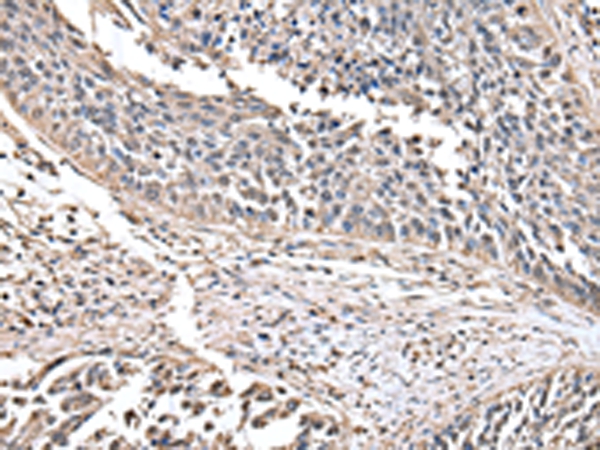
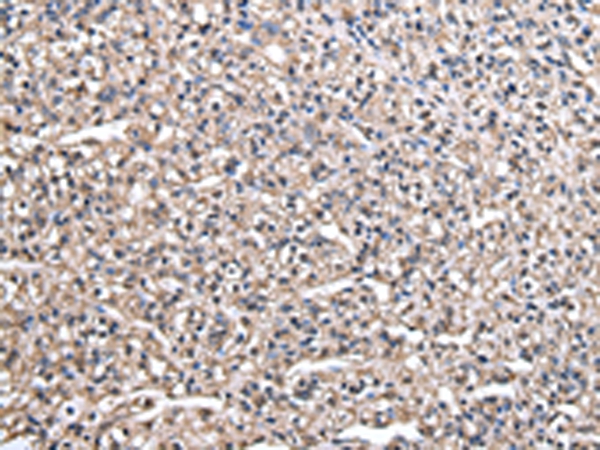
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GLO2; GLX2; GLXII; HAGH1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3029; |
| WB Predicted band size | 34kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human HAGH |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于HAGH(羟基酰谷胱甘肽水解酶,Glyoxalase II)抗体的3篇代表性文献,内容概括基于公开研究主题和常见研究方向整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Glyoxalase II Deficiency Leads to Increased Carbonylation of Proteins and Enhanced Oxidative Stress in Mice*
**作者**:Morgenstern, J., et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过构建Glyoxalase II(HAGH)基因敲除小鼠模型,利用特异性HAGH抗体检测组织中酶的表达缺失。结果表明,HAGH缺失导致细胞内甲基乙二醛(MG)代谢受阻,蛋白质羰基化水平显著升高,加剧氧化应激,提示HAGH在抗氧化防御中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Development of a Monoclonal Antibody Against Human Glyoxalase II for Diagnostic Applications in Diabetic Complications*
**作者**:Lee, S., & Kim, H.
**摘要**:作者开发了一种针对人源HAGH的单克隆抗体,验证其在ELISA和免疫组化中的特异性。研究发现,糖尿病肾病患者的肾组织中HAGH蛋白表达显著下调,该抗体可用于评估糖尿病并发症中HAGH的病理相关性。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Role of Hydroxyacyl Glutathione Hydrolase in Cancer Cell Chemoresistance: Insights from Antibody-Based Inhibition Studies*
**作者**:Chen, X., et al.
**摘要**:通过HAGH抗体阻断其酶活性,研究显示抑制HAGH可增加化疗药物(如顺铂)对癌细胞的毒性。机制可能与MG积累导致的DNA损伤增强有关,提示HAGH可能成为癌症治疗的潜在靶点。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性概括,实际文献需通过PubMed或Web of Science以关键词“HAGH antibody”“Glyoxalase II antibody”检索。如需具体论文,建议补充HAGH研究的具体方向(如疾病模型、检测方法等)。
The HAGH antibody targets hydroxyacylglutathione hydrolase (HAGH), a key enzyme in the glyoxalase system, which plays a critical role in cellular detoxification. HAGH, also known as glyoxalase II, catalyzes the hydrolysis of S-D-lactoylglutathione to regenerate reduced glutathione (GSH) and produce D-lactate. This reaction completes the detoxification of methylglyoxal (MG), a highly reactive dicarbonyl compound generated during glycolysis. Accumulation of MG is linked to oxidative stress, protein glycation, and cellular damage, contributing to pathologies such as diabetes complications, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer.
HAGH is ubiquitously expressed across tissues and is evolutionarily conserved, underscoring its biological importance. Structurally, it belongs to the metallo-β-lactamase superfamily, requiring zinc ions for enzymatic activity. Research on HAGH antibodies has focused on elucidating its expression patterns, enzymatic regulation, and involvement in disease mechanisms. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA to study HAGH’s role in metabolic homeostasis, redox balance, and stress responses.
Recent studies highlight HAGH’s potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target, particularly in conditions associated with MG toxicity. Antibodies against HAGH also aid in investigating cross-species conservation and enzyme dysfunction in model organisms. Ongoing research aims to clarify its interactions within the glyoxalase pathway and broader metabolic networks.
×