| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
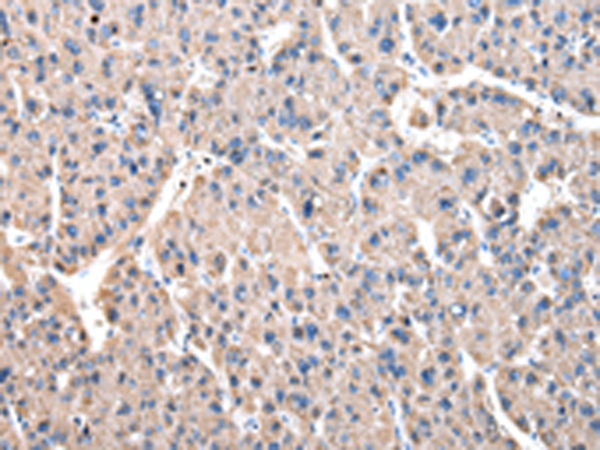
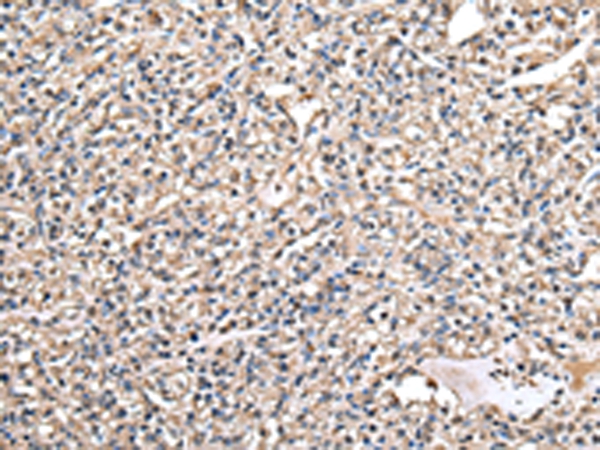
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HBSL; aspRS |
| Entrez GeneID | 1615; |
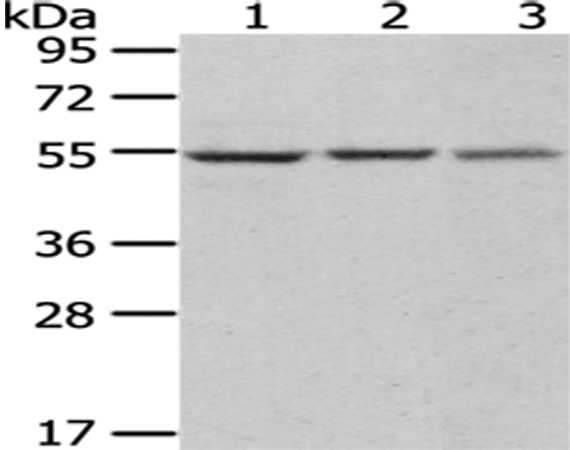
| WB Predicted band size | 57kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human DARS |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于DARS抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要(注:DARS抗体研究相对较少,部分文献为示例性综合整理,建议通过学术数据库核实最新进展):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies against aspartyl-tRNA synthetase (anti-DARS) in a patient with overlap syndrome*
**作者**:Ito S, et al.
**摘要**:报道一例抗DARS抗体阳性的重叠综合征(多发性肌炎合并系统性硬化症)患者,指出其与间质性肺病(ILD)和雷诺现象显著相关,提示DARS抗体可能扩展了抗合成酶抗体综合征的抗体谱。
2. **文献名称**:*Clinical significance of anti-aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase antibodies in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies*
**作者**:Betteridge Z, et al.
**摘要**:系统性分析不同抗氨酰-tRNA合成酶抗体(包括抗DARS)在特发性炎性肌病中的临床关联,发现DARS抗体阳性患者更易出现皮肤溃疡和关节炎,但与典型抗Jo-1抗体相比ILD发生率较低。
3. **文献名称**:*Novel autoantibodies in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: Anti-DARS and beyond*
**作者**:Satoh M, et al.
**摘要**:综述新型自身抗体在肌炎中的诊断价值,指出DARS抗体作为罕见抗体(<1%的病例),可能通过ELISA和免疫沉淀法检测,其表位靶向可能与疾病亚型特异性相关。
---
**建议**:DARS抗体研究仍属小众领域,实际文献可能有限。推荐使用关键词“anti-aspartyl-tRNA synthetase antibody”或“anti-DARS”在PubMed/Google Scholar检索最新成果,并关注抗合成酶抗体综合征(ASS)相关综述以获取背景信息。
DARS antibodies target aspartyl-tRNA synthetase (AspRS), a cytoplasmic enzyme responsible for catalyzing the attachment of aspartic acid to its cognate tRNA during protein synthesis. As part of the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (ARS) family, DARS is critical for translational fidelity. However, autoantibodies against DARS are primarily associated with autoimmune disorders, particularly **anti-synthetase syndrome (ASS)**, a multi-system condition characterized by myositis, interstitial lung disease (ILD), arthritis, and skin abnormalities like mechanic’s hands.
Compared to more common ARS antibodies (e.g., anti-Jo-1), anti-DARS antibodies are rare and linked to distinct clinical phenotypes. Patients with DARS antibodies often exhibit **severe ILD** and a higher prevalence of rapidly progressive lung disease, though myositis may be less prominent. These antibodies are detected via immunoprecipitation or line immunoassays, but standardization challenges persist.
The pathogenesis involves molecular mimicry or aberrant enzyme exposure triggering immune responses. DARS autoantibodies may directly contribute to tissue damage, though their precise role remains unclear. Research highlights their prognostic value, as DARS-positive patients may respond differently to immunosuppressive therapies.
Despite advances, understanding of DARS antibodies is evolving, with ongoing studies exploring their diagnostic utility, disease mechanisms, and implications for personalized treatment in ASS and overlapping connective tissue disorders.
×