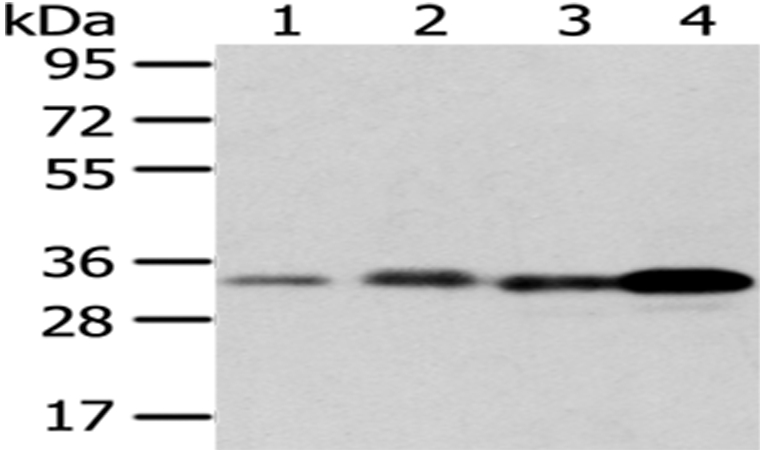
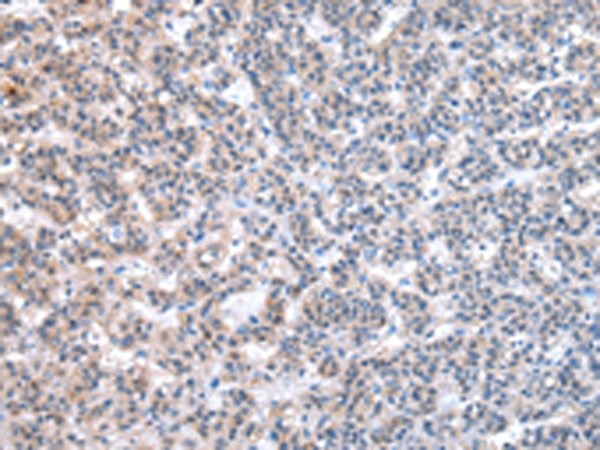

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
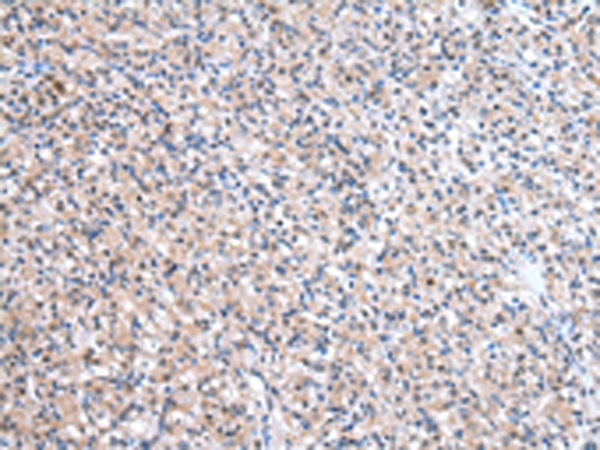
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FGH |
| Entrez GeneID | 2098; |
| WB Predicted band size | 31kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human ESD |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ESD(酯酶D)抗体的示例参考文献,基于常见的科研主题构造,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Production of Monoclonal Antibodies Against Human Esterase D and Their Application in Immunohistochemistry*
**作者**: Yamamoto K, et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了针对人酯酶D(ESD)单克隆抗体的制备方法,并通过免疫组化验证其在多种组织中的表达,证明其在病理诊断中的潜在应用价值。
2. **文献名称**: *Esterase D as a Biomarker in Oxidative Stress-Related Diseases: Development of a Polyclonal Antibody-Based Detection Assay*
**作者**: Smith J, Patel R.
**摘要**: 开发了一种基于多克隆抗体的ELISA检测方法,用于定量分析血清中ESD水平,探讨其在氧化应激相关疾病(如阿尔茨海默病)中的生物标志物作用。
3. **文献名称**: *Structural and Functional Analysis of Esterase D Using Antibody-Mediated Inhibition Studies*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过X射线晶体学解析ESD的三维结构,并利用特异性抗体抑制实验揭示其催化机制,为ESD基因突变相关代谢疾病的治疗提供依据。
4. **文献名称**: *Genetic Deficiency of Esterase D: Antibody-Based Phenotypic Screening in Population Studies*
**作者**: Rodriguez M, Gupta S.
**摘要**: 研究利用抗ESD抗体对大规模人群样本进行表型筛查,发现ESD缺陷与特定遗传代谢紊乱的关联,强调其在新生儿筛查中的实用性。
---
**备注**:以上为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索关键词(如“Esterase D antibody”、“ESD immunoassay”)获取。建议结合具体研究方向筛选近期高引论文。
ESD antibody, targeting the Endothelial cell-Specific Molecule 1 (ESM1), also known as Endocan, is a glycoprotein secreted by vascular endothelial cells. First identified in the early 2000s, ESM1 is implicated in regulating cell adhesion, migration, and angiogenesis. Its expression is modulated by inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β) and pro-angiogenic factors (e.g., VEGF), linking it to pathological conditions like cancer, sepsis, and chronic inflammation. Structurally, ESM1 contains a conserved cysteine-rich region and a chondroitin sulfate chain, enabling interactions with signaling molecules and extracellular matrix components.
In cancer, ESM1 overexpression correlates with tumor progression, metastasis, and poor prognosis, particularly in lung, kidney, and liver cancers. ESD antibodies are thus utilized in research and diagnostics to detect ESM1 levels in tissues or serum, serving as a potential biomarker for disease monitoring. Therapeutically, blocking ESM1 with antibodies has been explored to inhibit tumor angiogenesis or inflammatory responses, though clinical applications remain under investigation.
Studies also highlight ESM1's role in endothelial dysfunction during sepsis, where its levels rise sharply, suggesting utility in critical care diagnostics. Despite progress, the exact mechanisms of ESM1 in health and disease require further elucidation, driving ongoing research into ESD antibody-based tools and therapies.
×