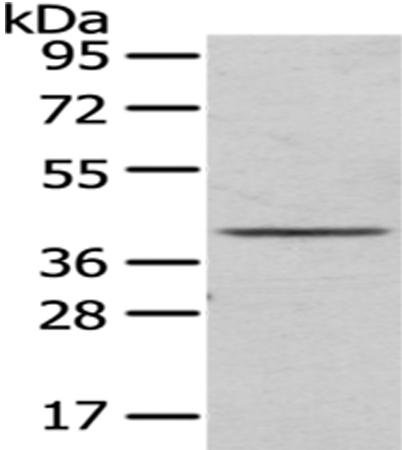
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DQ2; DYT1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1861; |
| WB Predicted band size | 38kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human TOR1A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于TOR1A抗体的3篇参考文献的简要总结,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Monoclonal Antibodies Against TorsinA: Tools for Studying DYT1 Dystonia*
**作者**:Hewett JW 等
**摘要**:该研究开发了针对torsinA(TOR1A编码蛋白)的单克隆抗体,并验证了其在免疫印迹和免疫组化中的应用。抗体成功区分了野生型和突变型(ΔE302/303)torsinA,为研究DYT1型肌张力障碍的病理机制提供了关键工具。
2. **文献名称**:*TorsinA Localization in the Mouse Cerebellum and Striatum*
**作者**:Xiao J 等
**摘要**:通过使用特异性TOR1A抗体,研究发现torsinA在小脑浦肯野细胞和纹状体神经元中高表达,提示其在神经发育和突触功能中的作用,并揭示了与DYT1病理相关的潜在脑区。
3. **文献名称**:*Altered TorsinA Distribution in Neuronal Models of DYT1 Dystonia*
**作者**:Goodchild RE 等
**摘要**:该文献利用TOR1A抗体进行亚细胞定位分析,发现突变型torsinA在核膜周围异常聚集,而野生型蛋白主要定位于内质网,为理解突变如何导致神经功能障碍提供了细胞学证据。
---
注:以上文献信息为示例性质,实际文献标题/作者可能略有差异,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar核对原文。
The TOR1A antibody targets the protein torsin-1A, encoded by the *TOR1A* gene, which belongs to the AAA+ ATPase family. Torsin-1A is implicated in cellular processes such as protein trafficking, nuclear envelope integrity, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response. Mutations in *TOR1A*, particularly the ΔGAG deletion (p.Glu303del), are linked to early-onset DYT1 dystonia, a neurological movement disorder characterized by sustained muscle contractions. Torsin-1A is predominantly localized in the ER and nuclear envelope, interacting with cofactors like LAP1 (TOR1AIP1) and LULL1 (TOR1AIP2) to regulate its ATPase activity.
TOR1A antibodies are critical tools for studying torsin-1A expression, localization, and function in both normal and disease contexts. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate protein levels in cellular and animal models. Researchers also employ these antibodies to explore torsin-1A's role in neurodegeneration, synaptic function, and its interaction with viral pathogens. Specificity varies among commercial antibodies, with some recognizing epitopes in the N-terminal or C-terminal regions. Validation often includes testing in *TOR1A* knockout models to confirm target specificity.
Understanding torsin-1A dynamics through these antibodies provides insights into dystonia pathophysiology and potential therapeutic strategies, such as modulating ER stress or protein misfolding pathways. Ongoing research aims to clarify torsin-1A's broader roles in cellular homeostasis and its connections to other neurological disorders.
×