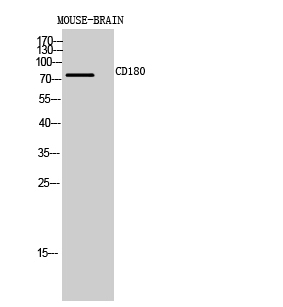
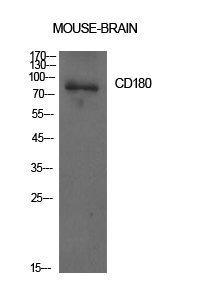
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD180; LY64; RP105; CD180 antigen; Lymphocyte antigen 64; Radioprotective 105 kDa protein; CD180 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4064; |
| WB Predicted band size | 75kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human CD180. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD180抗体的参考文献摘要:
1. **《CD180 functions as a TLR4 co-receptor in B cell activation》**
作者:A. M. B. York et al.
摘要:该研究揭示了CD180作为TLR4共受体在B细胞活化中的关键作用,通过抗体阻断实验证实其参与LPS介导的免疫信号传导,为B细胞相关疾病的治疗提供新靶点。
2. **《Anti-CD180 monoclonal antibody induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells》**
作者:K. R. Smith et al.
摘要:研究发现抗CD180单克隆抗体可通过激活Caspase通路诱导慢性淋巴细胞白血病(CLL)细胞凋亡,提示其作为潜在白血病治疗药物的可能性。
3. **《CD180 expression correlates with autoimmune disease severity in lupus models》**
作者:T. H. Lee & J. P. Müller
摘要:通过小鼠狼疮模型,证实CD180抗体检测可反映B细胞异常活化水平,其表达与肾脏损伤程度正相关,提示其作为系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)生物标志物的潜力。
以上文献涵盖了CD180在基础免疫机制、肿瘤治疗及自身免疫病中的研究,均涉及抗体实验验证功能或应用潜力。
CD180. also known as Ly64 or RP105. is a cell surface glycoprotein belonging to the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family. It lacks the intracellular Toll/IL-1 receptor (TIR) signaling domain, distinguishing it from canonical TLRs. Primarily expressed on B cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages, CD180 forms a heterodimer with MD-1. which stabilizes its surface expression and facilitates ligand recognition. While its exact ligands remain debated, CD180 is implicated in modulating innate immune responses and B-cell activation, survival, and antigen presentation.
CD180 antibodies are tools used to investigate its functional roles. Studies reveal that CD180 engagement can trigger signaling pathways, such as NF-κB and MAPK, influencing cytokine production and cell proliferation. In B-cell malignancies, altered CD180 expression has been observed, suggesting its potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target. Antibodies against CD180 are also employed in flow cytometry, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry to study its distribution and expression patterns in health and disease.
Notably, CD180 shares structural homology with TLR4 but appears to regulate TLR4 signaling indirectly, possibly acting as a decoy receptor. Its role in autoimmune diseases and infections is under exploration, with evidence linking CD180 dysfunction to impaired immune tolerance or pathogen response. Research using CD180 antibodies continues to clarify its dual regulatory/inhibitory functions, bridging innate and adaptive immunity.
×