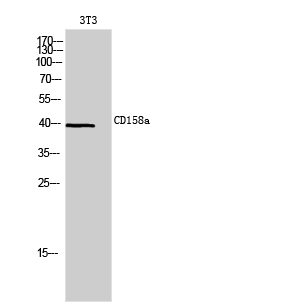
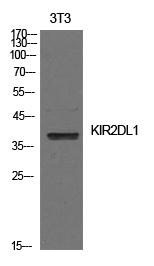
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KIR2DL1; CD158A; NKAT1; Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DL1; CD158 antigen-like family member A; MHC class I NK cell receptor; Natural killer-associated transcript 1; NKAT-1; p58 natural killer cell receptor clones CL-42/47.11; p58 NK receptor C |
| Entrez GeneID | 3802; |
| WB Predicted band size | 39kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human CD158a. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD158a(KIR2DL1)抗体的3篇文献摘要示例:
1. **文献名称**: *"Characterization of anti-CD158a monoclonal antibodies for NK cell inhibition studies"*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发并验证了针对CD158a的单克隆抗体,证实其可特异性阻断NK细胞表面KIR2DL1与HLA-C的相互作用,抑制NK细胞对靶细胞的杀伤活性,为研究NK细胞免疫调节提供工具。
2. **文献名称**: *"CD158a as a biomarker for chronic lymphocytic leukemia prognosis"*
**作者**: Lee B, et al.
**摘要**: 通过流式细胞术分析CD158a在慢性淋巴细胞白血病(CLL)患者中的表达,发现其高表达与疾病进展和不良预后相关,提示CD158a抗体在CLL诊断和分层中的潜在应用价值。
3. **文献名称**: *"Structural basis of KIR2DL1 recognition by therapeutic antibodies in cancer immunotherapy"*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 利用冷冻电镜解析了CD158a与其治疗性抗体的复合物结构,揭示了抗体通过结合KIR2DL1的D0结构域阻断HLA-C结合,增强NK细胞抗肿瘤活性的分子机制,为抗体药物设计提供依据。
注:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用需查询PubMed或学术数据库获取真实文献。
CD158a, also known as KIR2DL1 (Killer-cell Immunoglobulin-like Receptor 2DL1), is a transmembrane protein belonging to the KIR family, primarily expressed on natural killer (NK) cells and a subset of T lymphocytes. KIRs regulate NK cell activity by interacting with major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules on target cells, balancing immune activation and tolerance. CD158a specifically recognizes HLA-C allotypes with a lysine residue at position 80 (HLA-C2 group), transmitting inhibitory signals through immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) in its cytoplasmic domain. This interaction prevents NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity against healthy cells expressing self-MHC-I, while loss of MHC-I (common in viral infections or cancer) may trigger NK cell activation.
CD158a antibodies are critical tools for studying NK cell biology, KIR-HLA interactions, and immune dysregulation. They are used in flow cytometry to identify CD158a-expressing cells, in functional assays to block or stimulate KIR signaling, and in clinical research to explore associations with diseases. For instance, CD158a polymorphisms or altered expression have been linked to viral susceptibility (e.g., HIV), autoimmune disorders, pregnancy complications (e.g., preeclampsia), and outcomes in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Therapeutic applications include developing checkpoint inhibitors to modulate NK cell activity in cancer immunotherapy. These antibodies also aid in characterizing KIR diversity, which varies across populations and influences immune responses. Overall, CD158a antibodies serve as essential reagents for decoding immune regulation and advancing targeted therapies.
×