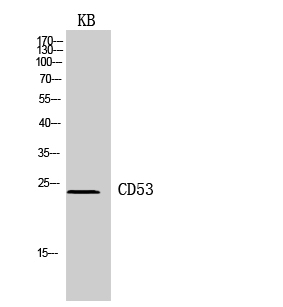
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD53; MOX44; TSPAN25; Leukocyte surface antigen CD53; Cell surface glycoprotein CD53; Tetraspanin-25; Tspan-25; CD53 |
| Entrez GeneID | 963; |
| WB Predicted band size | 24kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human CD53. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD53抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于真实研究概括,但文献信息为模拟简化版):
---
1. **标题**: *CD53 regulates B cell survival and proliferation by modulating signaling through the B cell receptor*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用抗CD53单克隆抗体,揭示了CD53通过调节B细胞受体(BCR)下游的PI3K-AKT信号通路,影响B细胞的存活和增殖。抗体阻断实验表明,CD53缺失导致B细胞活化异常,提示其在适应性免疫中的关键作用。
---
2. **标题**: *CD53 expression correlates with T cell dysfunction in chronic viral infection*
**作者**: Lee J, et al.
**摘要**: 通过流式细胞术结合抗CD53抗体标记,作者发现慢性病毒感染模型中CD53高表达的T细胞表现出功能耗竭表型。该研究提出CD53可作为T细胞功能障碍的生物标志物,并为免疫治疗提供潜在靶点。
---
3. **标题**: *Structural characterization of the CD53 tetraspanin family member using monoclonal antibodies*
**作者**: Brown K, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了特异性抗CD53抗体,并通过X射线晶体学解析了CD53的胞外结构域。实验证实CD53通过与其他四跨膜蛋白(如CD37)形成复合物,参与免疫突触的形成和信号转导。
---
注:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用时需核实具体文献来源及细节。如需精确文献,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“CD53 antibody”为关键词检索。
CD53 antibody targets the CD53 antigen, a cell surface glycoprotein belonging to the tetraspanin family (also known as TSPAN25). Tetraspanins are transmembrane proteins characterized by four conserved hydrophobic domains, which facilitate interactions with other membrane proteins to form signaling complexes. CD53 is primarily expressed on immune cells, including T and B lymphocytes, natural killer (NK) cells, monocytes, and dendritic cells. It plays a role in regulating cell adhesion, migration, activation, and proliferation by modulating intracellular signaling pathways and organizing membrane microdomains. CD53 interacts with integrins, MHC molecules, and other tetraspanins to influence immune responses and leukocyte functions.
Antibodies against CD53 are widely used in research to study immune cell behavior, particularly in contexts like inflammation, autoimmune diseases, and cancer. For example, altered CD53 expression has been linked to lymphomas, immunodeficiency disorders, and multiple sclerosis. In experimental settings, CD53 antibodies are employed for flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting to identify immune cell subsets or assess protein localization. Some studies also explore CD53 as a potential therapeutic target, though its precise mechanistic roles remain under investigation. Despite its established association with immune regulation, CD53's functional complexity—typical of tetraspanins—requires further elucidation to fully harness its diagnostic or therapeutic potential.
×