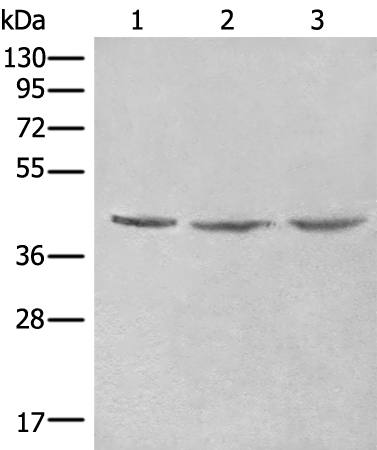
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
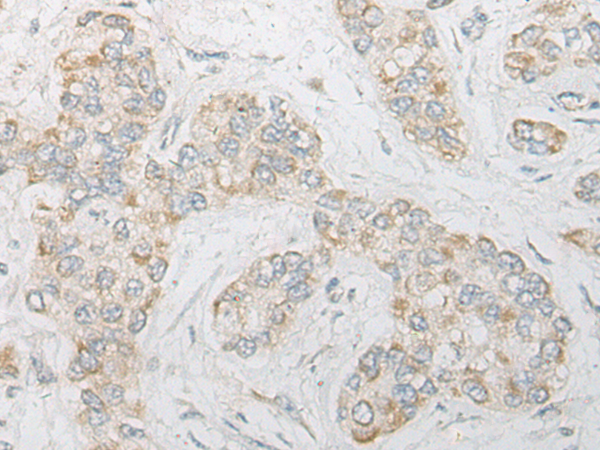
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CT1.11; MAGE11; MAGE-11; MAGEA-11 |
| WB Predicted band size | 48 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human MAGEA11 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于IL-1RII抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Interleukin-1 type II receptor: A decoy target for IL-1 that is regulated by IL-4"*
**作者**:Colotta, F. et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次提出IL-1RII作为IL-1信号通路的“诱饵受体”,其通过结合IL-1β抑制炎症反应。研究发现IL-4可上调IL-1RII的表达,并利用特异性抗体证实其阻断IL-1信号传导的机制。
2. **文献名称**:*"A monoclonal antibody to the human interleukin-1 receptor type II: Characterization and application in biological assays"*
**作者**:Symons, J.A. et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了一种针对人IL-1RII的单克隆抗体的开发,验证了其对IL-1RII的高亲和力及特异性,并证明该抗体可用于检测细胞表面及可溶性IL-1RII,为研究IL-1信号调控提供了工具。
3. **文献名称**:*"The soluble interleukin-1 receptor II (sIL-1RII) inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammation via membrane receptor shedding"*
**作者**:Banda, N.K. et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了IL-1RII通过金属蛋白酶(如ADAM17)介导的脱落形成可溶性受体(sIL-1RII),利用抗体阻断实验证明sIL-1RII可中和IL-1β活性,减轻炎症反应。
---
如需更多文献或具体应用场景,可进一步补充说明。
Interleukin-1 receptor type II (IL-1RII) is a decoy receptor within the IL-1 receptor family, primarily involved in regulating IL-1-mediated inflammatory responses. Unlike the signaling receptor IL-1RI, IL-1RII lacks a functional Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain, rendering it incapable of initiating intracellular signaling. It binds IL-1β and IL-1α with high affinity, sequestering these pro-inflammatory cytokines and preventing their interaction with IL-1RI, thereby dampening inflammation. IL-1RII exists in both membrane-bound and soluble forms, the latter generated through proteolytic cleavage or alternative splicing. Its expression is upregulated in various immune cells, including monocytes and neutrophils, as well as in tissues during inflammatory or autoimmune conditions.
Antibodies targeting IL-1RII are valuable tools for studying its regulatory role in inflammation, immune homeostasis, and disease pathogenesis. These antibodies enable detection of IL-1RII expression in cells or tissues via techniques like flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, or Western blotting. Neutralizing antibodies can block IL-1RII’s ligand-binding capacity, facilitating research into IL-1 signaling dynamics. In therapeutic contexts, IL-1RII antibodies have been explored for modulating excessive IL-1 activity, which is implicated in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, sepsis, and atherosclerosis. However, therapeutic applications remain limited compared to direct IL-1 inhibitors, as IL-1RII’s role as a natural brake on inflammation makes it a complex target. Current research focuses on understanding its dual role in resolving inflammation and potential immune evasion mechanisms in chronic diseases.
×