
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
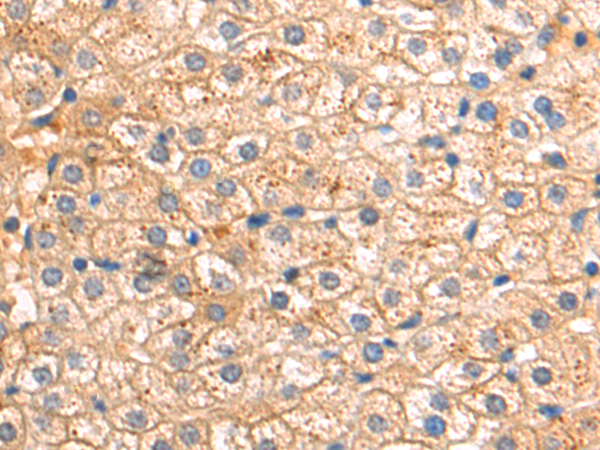
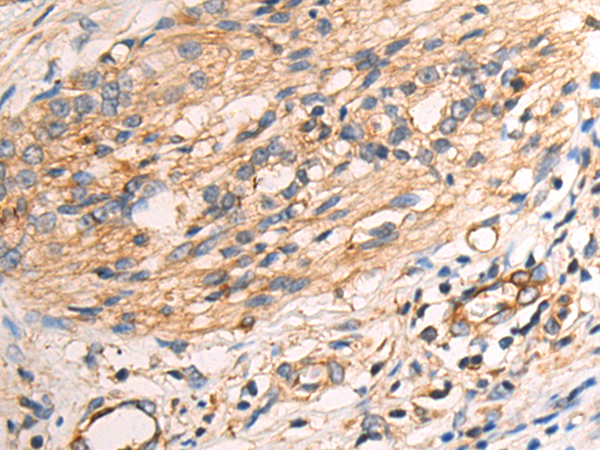
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CT1.8; MAGE8 |
| WB Predicted band size | 35 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human MAGEA8 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD74抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容的简要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD74 in B-cell malignancies with milatuzumab—a humanized anti-CD74 antibody*
**作者**:Stein R, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了人源化抗CD74抗体(milatuzumab),并证明其在非霍奇金淋巴瘤等B细胞恶性肿瘤中具有治疗潜力。实验显示,该抗体通过诱导内化和凋亡抑制肿瘤细胞生长,且在动物模型中表现出显著抗肿瘤活性。
2. **文献名称**:*Structural analysis of HLA-DR-bound peptides reveals mechanisms of antigen presentation by CD74*
**作者**:Natarajan K, et al.
**摘要**:文章通过X射线晶体学解析了CD74与HLA-DR复合物的结构,揭示了CD74作为MHC II类分子伴侣在抗原呈递中的关键作用。研究利用抗体阻断实验验证了CD74在调节抗原肽装载中的功能。
3. **文献名称**:*CD74-MIF signaling drives NF-κB activation in B-cell survival and lymphomagenesis*
**作者**:Starlets D, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现CD74与巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子(MIF)结合后激活NF-κB通路,促进B细胞存活及淋巴瘤发生。抗CD74抗体可阻断该通路,为靶向CD74-MIF轴的癌症治疗提供依据。
---
以上文献涵盖了CD74抗体在肿瘤治疗、抗原呈递机制及信号通路调控中的应用,均为该领域的代表性研究。
CD74. also known as the invariant chain (Ii), is a transmembrane glycoprotein that primarily functions as a chaperone for major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC II) molecules. Discovered in the 1970s, CD74 plays a critical role in antigen presentation by stabilizing MHC II during its transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to endosomal compartments, preventing premature binding of antigens. It is expressed in antigen-presenting cells, including B cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages. Proteolytic cleavage of CD74 in endosomes releases MHC II for peptide loading, a key step in adaptive immune responses.
CD74 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions. They are widely used in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting to investigate immune cell biology and diseases. Beyond research, CD74 has therapeutic relevance. It is overexpressed in certain cancers (e.g., lymphoma, melanoma) and autoimmune disorders, making it a potential therapeutic target. Antibodies like milatuzumab (anti-CD74) are being explored in clinical trials for hematologic malignancies, leveraging CD74's role in cell survival and proliferation via pathways like NF-κB.
Additionally, CD74 interacts with the cytokine macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), influencing inflammatory responses and tumor progression. This dual role in immunity and disease underscores its significance as both a biomarker and a target for immunotherapy.
×