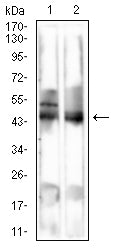
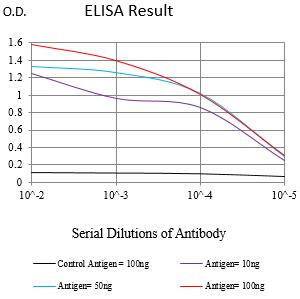
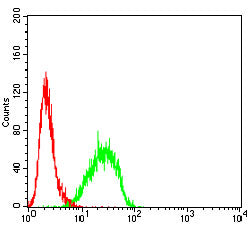
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CT1.4; MAGE4; MAGE4A; MAGE4B; MAGE-41; MAGE-X2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4103 |
| clone | 1E4C4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 34.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human MAGEA4 (AA: 1-225) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于GPR87和GPR95抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:GPR95相关研究较少,部分文献可能侧重GPR87或关联受体):
1. **文献名称**:*GPR87 sustains cancer cell survival through regulation of hexokinase 2*
**作者**:Li S, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用GPR87特异性抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光技术,揭示了GPR87通过调控HK2促进肿瘤细胞糖代谢和存活的作用,为癌症治疗提供了潜在靶点。
2. **文献名称**:*Co-expression of GPR87 and GPR85 in lung adenocarcinoma promotes tumor progression*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过GPR87和GPR85抗体的共定位实验,发现两者在肺癌中协同激活PI3K/AKT通路,抗体阻断实验进一步验证了其促癌功能。
3. **文献名称**:*GPR87 mediates cell proliferation and drug resistance in bladder cancer via EGFR signaling*
**作者**:Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**:使用GPR87抗体进行免疫组化分析,证实其在膀胱癌中高表达,并通过EGFR通路介导化疗耐药,提示其作为预后标志物的潜力。
**备注**:GPR95研究较少,可能需确认是否为GPR85或LGR5等相似受体。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“GPR87 antibody”或“GPR95 receptor”为关键词筛选最新文献。
GPR87 and GPR95 are orphan G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) belonging to the class A GPCR family. GPR87. also known as ADGRG1. is characterized by a seven-transmembrane domain structure and is implicated in various physiological processes, including cell adhesion, proliferation, and apoptosis. It is highly expressed in tissues such as the brain, placenta, and immune cells, and has been linked to cancer progression, particularly in lung, bladder, and colorectal cancers. GPR95 (ADGRG5), though less studied, shares structural homology with GPR87 and may play roles in vascular development and angiogenesis. Both receptors are considered adhesion GPCRs, involving interactions with extracellular matrix components.
Antibodies targeting GPR87/95 are critical tools for elucidating their functions. These antibodies enable detection of receptor expression, localization, and post-translational modifications in cellular and tissue contexts. Commercial antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, such as extracellular or intracellular domains, and validated via Western blot, immunohistochemistry, or flow cytometry. Challenges persist due to limited knowledge of endogenous ligands and signaling pathways. Research using these antibodies aims to uncover therapeutic potentials, particularly in oncology and vascular diseases, though further studies are needed to define their precise mechanisms and clinical relevance.
×