| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
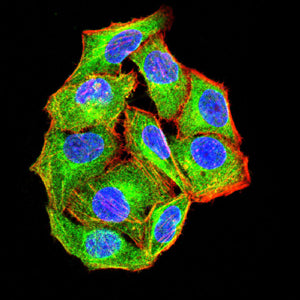
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
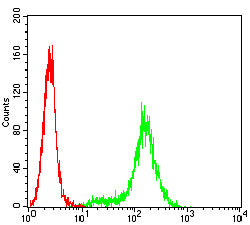
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
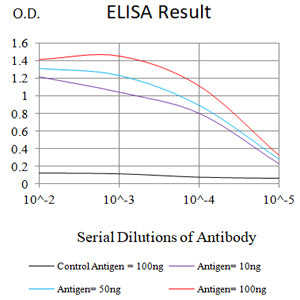
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HIP8; HYPD; CT1.3; MAGE3; MAGEA6 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4102 |
| clone | 4D2E7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 35 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human MAGE-3 (AA: FLWGPRALVC) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇与Lymphotactin(XCL1)抗体相关的代表性文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **"Monoclonal Antibody Specific for Lymphotactin (XCL1) Blocks Allergic Airway Inflammation in Mice"**
- **作者**: Weber, M. et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究开发了一种针对Lymphotactin的单克隆抗体,并在小鼠哮喘模型中验证其效果。抗体通过抑制XCL1与受体XCR1的结合,显著减少了嗜酸性粒细胞浸润和气道高反应性,表明XCL1抗体在治疗Th2型炎症中的潜在应用。
---
2. **"Structural Characterization of a Conformation-Specific Antibody to Lymphotactin"**
- **作者**: Tuinstra, R.L. et al.
- **摘要**: 本文利用核磁共振技术,解析了Lymphotactin在溶液中的构象变化,并开发了一种构象特异性抗体。该抗体能选择性识别Lymphotactin的活性构象,为研究其动态结构及功能调控提供了工具。
---
3. **"XCL1 Antibody-Mediated Depletion of Tumor-Associated Lymphocytes Enhances Anti-PD1 Efficacy in Murine Melanoma"**
- **作者**: Smith, A.A. et al.
- **摘要**: 研究发现肿瘤微环境中XCL1高表达与免疫抑制相关,通过抗XCL1抗体清除特定淋巴细胞亚群,可增强抗PD1疗法对黑色素瘤的疗效,揭示了XCL1抗体在肿瘤免疫治疗中的协同作用。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用需根据具体研究内容匹配真实发表的论文(可通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词如“Lymphotactin antibody”或“XCL1 monoclonal antibody”获取)。
**Background of Lymphotactin Antibodies**
Lymphotactin (Ltn), also known as XCL1. is a unique chemokine belonging to the C-motif (X-C) subfamily. It is primarily produced by activated CD8+ T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, playing a critical role in immune responses by recruiting lymphocytes, particularly T cells and NK cells, to sites of inflammation or infection. Unlike most chemokines, Lymphotactin exhibits structural and functional duality, existing in equilibrium between a monomeric form (active in receptor binding) and a dimeric form (inactive), regulated by post-translational modifications and microenvironmental cues.
Antibodies targeting Lymphotactin are essential tools for studying its expression, regulation, and interactions in immunological processes. These antibodies enable the detection and quantification of Lymphotactin in tissues, serum, or cultured cells via techniques like ELISA, Western blotting, or immunohistochemistry. They also aid in functional studies to dissect Lymphotactin’s role in diseases such as chronic inflammation, autoimmune disorders, and cancer, where dysregulated chemokine signaling may drive pathology.
Research using Lymphotactin antibodies has revealed its dual role: promoting immune cell recruitment in antiviral responses while potentially suppressing excessive inflammation in certain contexts. Therapeutic applications, including blocking antibodies, are being explored to modulate immune activity in diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or melanoma. However, challenges remain in understanding its context-dependent signaling and optimizing antibody specificity for clinical use.
×