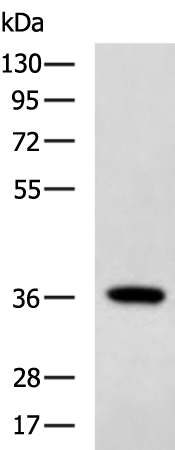
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CT1.2; MAGE2; MAGEA2A |
| WB Predicted band size | 35 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human MAGEA2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于泛素(Ub)抗体的参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **《Ubiquitin: structures, functions, mechanisms》**
*作者:Hershko, A., & Ciechanover, A. (2000).*
**摘要**:该综述系统阐述了泛素的结构、功能及其介导的蛋白质降解机制,重点讨论了泛素化在细胞周期调控、DNA修复和疾病中的关键作用,并提及泛素抗体在相关研究中的应用。
2. **《Ubiquitin and Parkinson's disease: Implications for therapeutic intervention》**
*作者:Lowe, J., et al. (2007).*
**摘要**:研究通过泛素抗体检测帕金森病患者脑组织中的Lewy小体,发现异常泛素化蛋白聚集与疾病进展相关,为神经退行性疾病的病理机制提供了分子依据。
3. **《Detection of ubiquitinated proteins in Alzheimer's disease using monoclonal antibodies》**
*作者:Perry, G., et al. (1987).*
**摘要**:早期研究利用泛素特异性单克隆抗体,揭示了阿尔茨海默病患者脑内神经纤维缠结中存在泛素化tau蛋白,为异常蛋白沉积的病理研究奠定了基础。
4. **《The role of ubiquitin in DNA repair: focus on ubiquitin-like modifications》**
*作者:Dantuma, N. P., & van Attikum, H. (2016).*
**摘要**:探讨泛素及泛素样修饰在DNA损伤修复中的调控作用,通过泛素抗体的应用,解析了修复复合体的动态组装机制及其与癌症治疗的联系。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用时需核对期刊名称、年份及具体内容。若需更精准的文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“ubiquitin antibody”“ubiquitin detection”等关键词检索。
Ubiquitin (Ub) antibodies are essential tools in studying the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS), a critical pathway for protein degradation in eukaryotic cells. Ubiquitin, a small regulatory protein, is covalently attached to substrate proteins via a process called ubiquitination, marking them for proteasomal degradation or modulating their activity, localization, or interactions. This post-translational modification is mediated by a cascade of enzymes (E1. E2. E3) and is reversible through deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs). Dysregulation of ubiquitination is implicated in numerous diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and autoimmune conditions.
Ub antibodies are widely used in research to detect ubiquitinated proteins, map ubiquitination sites, and investigate UPS dynamics. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies target distinct epitopes, such as free ubiquitin, ubiquitin chains (e.g., K48- or K63-linked), or ubiquitin-like proteins (e.g., SUMO or NEDD8). Applications include Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence. Specific Ub antibodies help identify disease-associated ubiquitination patterns, such as aggregated ubiquitin-positive inclusions in Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease.
Recent advancements in proteomics and structural biology have driven the development of highly specific Ub antibodies, enabling precise analysis of chain topology and substrate recognition. These tools are vital for unraveling the complexity of ubiquitin signaling and developing targeted therapies, such as proteasome inhibitors or E3 ligase modulators, in precision medicine.
×