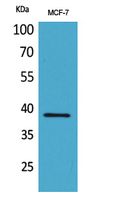
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CER1; DAND4; Cerberus; Cerberus-related protein; DAN domain family member 4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9350; |
| WB Predicted band size | 30kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human Cerberus. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及Cerberus抗体的经典文献及摘要内容:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Cerberus is a head-inducing secreted factor expressed in the anterior endoderm of Spemann’s organizer*
**作者**: Bouwmeester, T., Kim, S., Sasai, Y., Lu, B., & De Robertis, E.M.
**摘要**: 该研究首次克隆了非洲爪蟾(*Xenopus*)中的Cerberus基因,发现其编码一种分泌蛋白,可拮抗BMP、Wnt和Nodal信号通路。文中提到通过制备特异性多克隆抗体,证实Cerberus蛋白在早期胚胎的前端内胚层中表达,并参与头部组织的诱导。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Cerberus regulates left-right asymmetry of the embryonic body plan*
**作者**: Belo, J.A., Bouwmeester, T., Leyns, L., Kertesz, N., Gallo, M., & Steinbeisser, H.
**摘要**: 本研究利用小鼠模型,发现Cerberus的同源基因Cer-l在胚胎左侧中胚层中表达,调控左右不对称发育。作者使用抗Cer-l抗体进行原位杂交和免疫组化,证明其蛋白定位对心脏和内脏器官的左右轴形成至关重要。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Distinct roles of the secreted proteins CHORDIN and CERBERUS in head induction*
**作者**: Piccolo, S., Agius, E., Leyns, L., Bhattacharyya, S., Grunz, H., & De Robertis, E.M.
**摘要**: 文章比较了Chordin和Cerberus在头部诱导中的功能差异,发现Cerberus通过同时抑制BMP和Wnt信号促进前脑发育。研究中通过抗体阻断实验证实,Cerberus的活性依赖于其N端结构域,且其表达受上游信号因子的精确调控。
---
这些文献均为早期发育生物学领域的经典研究,重点解析Cerberus蛋白的功能及其抗体的应用。如需更近期研究,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中检索关键词“Cerberus antibody + 应用领域(如癌症、干细胞)”。
Cerberus antibodies are tools used to study the Cerberus protein, a key regulator in embryonic development. Named after the multi-headed hound of Greek mythology, Cerberus was first identified in Xenopus (frog) and mouse models as a secreted inhibitor of Nodal, BMP, and Wnt signaling pathways. These pathways are critical for establishing the body plan during early embryogenesis, particularly in anterior-posterior axis formation and left-right asymmetry. The Cerberus protein, expressed in the anterior visceral endoderm and primitive streak, acts as a multifunctional antagonist, ensuring proper organogenesis, especially in the heart and head regions.
Antibodies targeting Cerberus enable researchers to visualize its spatiotemporal expression via techniques like immunohistochemistry or Western blotting. They also facilitate functional studies by blocking or tracking Cerberus activity in developmental models. Such research has clarified Cerberus's role in stem cell differentiation, tissue patterning, and congenital defects. Additionally, Cerberus antibodies have been employed in regenerative medicine and cancer studies, as dysregulation of its associated pathways may contribute to tumorigenesis. Despite its transient expression in early embryos, Cerberus remains a pivotal model for understanding extracellular signaling crosstalk. These antibodies continue to bridge developmental biology with therapeutic exploration.
×