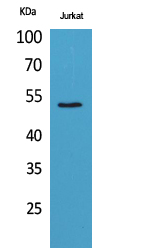
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TUBA1A; TUBA3; Tubulin alpha-1A chain; Alpha-tubulin 3; Tubulin B-alpha-1; Tubulin alpha-3 chain; TUBA1B; Tubulin alpha-1B chain; Alpha-tubulin ubiquitous; Tubulin K-alpha-1; Tubulin alpha-ubiquitous chain; TUBA1C; TUBA6; |
| Entrez GeneID | 7846; |
| WB Predicted band size | 50kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human Tubulin α around the non-acetylation site of K40. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Tubulin α抗体的参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容概括列出:
---
1. **文献名称**: "Monoclonal antibodies specific for α-tubulin subtypes demonstrate differential microtubule organization in diverse eukaryotic cells"
**作者**: Piperno G., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用针对不同α-tubulin亚型的单克隆抗体,揭示了真核生物(包括哺乳动物和原生生物)中微管蛋白亚型的分布差异,并证明其在纤毛形成和细胞分裂中的特异性功能。
2. **文献名称**: "α-Tubulin acetylation distinguishes dynamic microtubules in cortical neurons and affects axonal outgrowth"
**作者**: Hammond J.W., et al.
**摘要**: 通过特异性抗体检测α-微管蛋白的乙酰化修饰,研究发现神经元轴突中高乙酰化的微管具有更高的稳定性,这一特性对轴突生长和神经发育至关重要。
3. **文献名称**: "A standardized protocol for using α-tubulin antibodies in cancer cell biology studies"
**作者**: Gundersen G.G., Bulinski J.C.
**摘要**: 提出了一种基于α-tubulin抗体的标准化实验流程,用于分析癌细胞中微管网络的动态变化,并验证其在药物筛选和肿瘤迁移研究中的可靠性。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性概括,实际引用时需核对原文信息及期刊准确性。建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以关键词“α-tubulin antibody”或“anti-α-tubulin”检索最新研究。
Tubulin α antibodies are essential tools in cellular and molecular biology research, targeting the α-subunit of tubulin, a key component of microtubules. Tubulin exists as α/β heterodimers that polymerize into dynamic microtubules, crucial for maintaining cell shape, intracellular transport, and chromosome segregation during mitosis. The α-tubulin subunit, encoded by genes like TUBA1A, is highly conserved across eukaryotes and plays a structural role in microtubule assembly.
These antibodies are widely used to study microtubule organization, cell cycle dynamics, and cytoskeletal changes in processes like differentiation, migration, or disease. In techniques such as Western blot, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry, they help quantify tubulin expression or visualize microtubule networks. Notably, α-tubulin antibodies often serve as loading controls due to the protein’s consistent expression in most cells.
Specificity varies: some antibodies detect pan-α-tubulin, while others target post-translational modifications (e.g., acetylation, detyrosination) or isoforms (e.g., TUBA1A, TUBA4A), which have tissue-specific roles. For instance, α-tubulin III (TUBA1A) marks neurons, aiding neurological studies. Dysregulated α-tubulin expression or altered microtubule stability is linked to cancers, neurodegenerative diseases, and ciliopathies, making these antibodies valuable in pathological research and drug development (e.g., studying taxane-based chemotherapeutics). Cross-reactivity with species like human, mouse, and rat enhances their utility across experimental models.
×