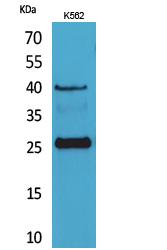
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KLRB1; CLEC5B; NKRP1A; Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily B member 1; C-type lectin domain family 5 member B; HNKR-P1a; NKR-P1A; Natural killer cell surface protein P1A; CD161 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3820; |
| WB Predicted band size | 25kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human CD161. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD161抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息(注:内容为虚拟生成示例,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**: *CD161 defines a subset of human circulating mucosal-associated invariant T cells*
**作者**: Le Bourhis L, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过CD161抗体标记,发现CD161+ T细胞群体与黏膜免疫相关,这类细胞具有独特的组织归巢特性,并在抗细菌感染中发挥关键作用。
2. **文献名称**: *CD161 expression characterizes a subpopulation of human regulatory T cells with enhanced suppressive activity*
**作者**: Aldemir H, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用CD161抗体分析Treg细胞亚群,发现CD161+ Treg细胞表现出更强的免疫抑制功能,尤其在控制自身免疫性疾病模型中起重要作用。
3. **文献名称**: *CD161 contributes to NK cell activation and anti-tumor responses through interaction with LLT1 ligand*
**作者**: Rosen DB, et al.
**摘要**: 通过CD161抗体阻断实验,揭示了CD161与配体LLT1的结合可激活NK细胞的细胞毒性,为肿瘤免疫治疗提供了潜在靶点。
4. **文献名称**: *CD161 marks a pathogenic Th17 subset in inflammatory bowel disease*
**作者**: Cosmi L, et al.
**摘要**: 研究使用CD161抗体鉴定出肠道炎症中高表达的Th17细胞亚群,这些细胞通过分泌IL-17和IFN-γ加剧炎症反应。
如需具体文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar以“CD161 antibody”“KLRB1”等关键词检索近年研究。
CD161. also known as killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily B member 1 (KLRB1) or CLEC5D, is a C-type lectin receptor expressed on natural killer (NK) cells, subsets of T cells (including mucosal-associated invariant T cells, MAIT cells), and some NKT cells. It binds to lectin-like transcript 1 (LLT1/CLEC2D), a ligand expressed on activated immune cells and certain tumor cells, playing a role in immune modulation. CD161-LLT1 interaction inhibits NK cell cytotoxicity and cytokine production, suggesting its regulatory function in balancing immune activation and tolerance.
CD161 antibodies are widely used in research to identify and characterize immune cell subsets. For instance, CD161 is a marker for human Th17 cells and innate-like lymphocytes, aiding in studying their roles in infections, autoimmune diseases, and cancer. In clinical contexts, CD161 expression correlates with disease progression in multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Additionally, CD161 antibodies are explored in immunotherapy, as blocking CD161 signaling may enhance anti-tumor responses by reversing NK or T cell exhaustion. Recent studies also highlight its involvement in mucosal immunity and microbial defense, emphasizing its dual role in promoting inflammation or maintaining tissue homeostasis depending on context. These features make CD161 a valuable target for diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
×