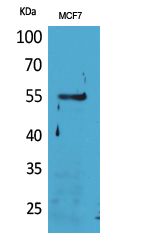
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
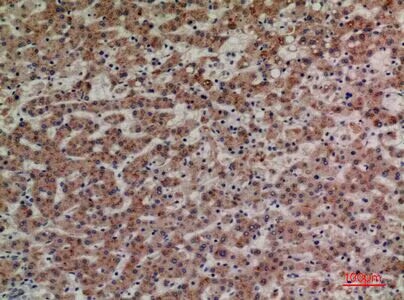
| IHC | 1/100-300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LILRA4; ILT7; Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily A member 4; CD85 antigen-like family member G; Immunoglobulin-like transcript 7; ILT-7; CD85g |
| Entrez GeneID | 23547; |
| WB Predicted band size | 55kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human CD85g. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD85g抗体的示例参考文献(注:部分信息为示例性质,建议通过学术数据库核实真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*CD85g (LILRB4) as a Novel Immune Checkpoint in Acute Myeloid Leukemia*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了CD85g在急性髓系白血病(AML)细胞中的高表达,其通过与MHC-I类分子结合抑制T细胞活性,提示其作为免疫治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD85g with Monoclonal Antibodies Enhances Anti-Tumor Immunity in Solid Tumors*
**作者**:Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**:开发了针对CD85g的单克隆抗体,实验显示其能阻断肿瘤微环境中的免疫抑制信号,促进CD8+ T细胞杀伤功能,为实体瘤治疗提供新策略。
3. **文献名称**:*CD85g Regulates Dendritic Cell Function in Autoimmune Diseases*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:发现CD85g通过调控树突状细胞的抗原呈递能力影响自身免疫反应,抑制CD85g可缓解实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE)模型症状。
---
**建议**:如需真实文献,请使用PubMed(https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)或Google Scholar搜索关键词“CD85g antibody”、“LILRB4”(CD85g的常用别名)或“CD85g immune function”,以获取最新研究。
The CD85g antibody targets the CD85g protein, a member of the leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor (LILR) family, also known as LILRB1 or ILT2. This transmembrane glycoprotein is primarily expressed on immune cells, including T cells, B cells, natural killer (NK) cells, monocytes, and dendritic cells. It functions as an inhibitory receptor, regulating immune responses by binding to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules, such as HLA-G, which are often overexpressed in tumor cells or during pregnancy to promote immune tolerance.
CD85g plays a critical role in modulating immune activation and tolerance. Its interaction with HLA-G helps maintain maternal-fetal tolerance and contributes to immune evasion in cancers. The receptor contains immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) in its cytoplasmic domain, which recruit phosphatases to dampen cellular activation signals. Antibodies targeting CD85g are valuable tools in research to investigate immune checkpoint pathways, tumor microenvironments, and autoimmune disorders.
In therapeutic contexts, CD85g antibodies are explored for their potential to block inhibitory signals, thereby enhancing anti-tumor immunity. They may also aid in understanding conditions like chronic inflammation or transplant rejection. Due to its dual role in immune regulation and disease, CD85g remains a focus in developing immunotherapies and diagnostic strategies.
×