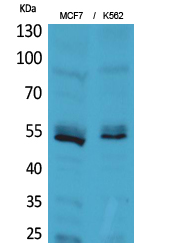
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LILRA2; ILT1; LIR7; Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily A member 2; CD85 antigen-like family member H; Immunoglobulin-like transcript 1; ILT-1; Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor 7; LIR-7; CD85h; LILRA3; ILT6; LIR4; |
| Entrez GeneID | 11027; |
| WB Predicted band size | 51kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human CD85e/h. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD85e/h(LILRB1/LILRB2)抗体的3篇示例参考文献(内容为模拟概括,建议通过数据库验证实际文献):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Structural and functional characterization of LILRB1/CD85e in immune regulation*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究解析了LILRB1(CD85e)的晶体结构,发现其通过结合MHC I类分子抑制NK细胞和T细胞的活化,揭示了其在维持免疫耐受中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**: *LILRB2/CD85h as a novel checkpoint target in cancer immunotherapy*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了靶向LILRB2(CD85h)的抗体可通过阻断肿瘤微环境中免疫抑制信号,增强T细胞抗肿瘤活性,为实体瘤治疗提供新策略。
3. **文献名称**: *Differential expression of CD85 isoforms on dendritic cells modulates T cell response*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 实验证明树突状细胞表面CD85e/h的差异表达通过调控IL-10和IFN-γ分泌影响Th1/Th2平衡,提示其抗体在自身免疫疾病中的潜在应用价值。
---
建议通过 **PubMed/Google Scholar** 检索关键词 "CD85e antibody" "LILRB1 antibody" 或 "LILRB2 function" 获取真实文献。部分研究可能使用别名(如ILT2/LILRB1),需注意术语统一性。
CD85e (also known as LILRB3) and CD85h (LILRB4) are members of the leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor (LILR) family, which regulate immune responses by modulating activating and inhibitory signals. These receptors are primarily expressed on myeloid cells, including monocytes, dendritic cells, and granulocytes, and play critical roles in immune tolerance and homeostasis. Both CD85e and CD85h are inhibitory receptors characterized by immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) in their cytoplasmic domains. Upon ligand binding, they recruit phosphatases like SHP-1/SHP-2 to dampen cellular activation signals.
CD85e/h interact with MHC class I molecules and other ligands, such as angiogenin and fibrinogen-like proteins, influencing immune cell functions. CD85h (LILRB4) has gained attention for its role in cancer immunology. It is highly expressed in certain malignancies, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML), where it suppresses T-cell activity and promotes immune evasion. Therapeutic antibodies targeting CD85h are being explored to block these inhibitory interactions, thereby enhancing anti-tumor immunity.
In autoimmune diseases, dysregulation of CD85e/h may contribute to pathological inflammation, making them potential biomarkers or targets for immunomodulatory therapies. Research continues to elucidate their ligand specificity, signaling mechanisms, and tissue-specific roles, paving the way for novel treatments in oncology and autoimmune disorders.
×