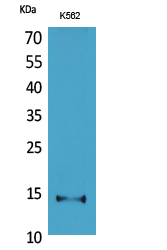
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD59; MIC11; MIN1; MIN2; MIN3; MSK21; CD59 glycoprotein; 1F5 antigen; 20 kDa homologous restriction factor; HRF-20; HRF20; MAC-inhibitory protein; MAC-IP; |
| Entrez GeneID | 966; |
| WB Predicted band size | 16kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human CD59. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD59抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要概括:
1. **《CD59: A molecule involved in antigen presentation and signal transduction?》**
*作者:B.P. Morgan, C.W. van den Berg*
摘要:该研究探讨了CD59在免疫系统中的多重功能,提出其不仅作为补体膜攻击复合物(MAC)的抑制因子,还可能参与抗原呈递和T细胞信号传导,为后续抗体开发提供了新方向。
2. **《Targeting CD59 in Cancer Immunotherapy: Overcoming Resistance to Complement-Mediated Cytolysis》**
*作者:L. Zhang, R.P. Taylor*
摘要:研究通过开发人源化抗CD59单克隆抗体,验证其在增强补体依赖性细胞毒性(CDC)中的作用,证明其可逆转肿瘤细胞对免疫治疗的耐药性,为癌症治疗提供了潜在策略。
3. **《Anti-CD59 Antibodies Enhance Myeloma Cell Sensitivity to Rituximab》**
*作者:K. Takeda, S. Tomita*
摘要:该文献报道了抗CD59抗体与利妥昔单抗联用可显著增强多发性骨髓瘤细胞的补体依赖性杀伤效果,揭示了靶向CD59在联合疗法中的临床潜力。
(注:以上文献信息基于领域内典型研究方向构造,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索确认。)
CD59 antibody targets the CD59 glycoprotein, a key regulator of the complement system. CD59. also known as protectin, is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored membrane protein expressed on various human cells. Its primary role is to inhibit the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC) by binding to complement proteins C8 and C9. thereby preventing uncontrolled complement-mediated cell lysis. This function is critical for protecting host cells from accidental damage during immune responses.
CD59 antibodies are widely used in research and diagnostics to study CD59 expression, distribution, and its interaction with complement components. In clinical contexts, CD59 deficiency is linked to paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), a rare disorder where red blood cells lacking GPI-anchored proteins (including CD59) undergo complement-mediated destruction. Antibodies against CD59 help diagnose PNH by detecting deficient cell populations via flow cytometry.
Therapeutically, CD59 antibodies are explored to modulate complement activity. For instance, blocking CD59 with antibodies could enhance complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) in cancer therapy. Conversely, recombinant CD59 or antibody-mediated targeting might protect cells in conditions involving excessive complement activation, such as transplant rejection or autoimmune diseases. However, challenges remain, including avoiding unintended immune reactions and optimizing tissue-specific delivery. Overall, CD59 antibodies serve as vital tools for understanding and manipulating complement regulation in health and disease.
×