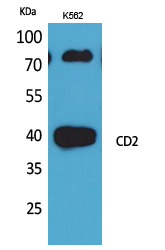
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD2; SRBC; T-cell surface antigen CD2; Erythrocyte receptor; LFA-2; LFA-3 receptor; Rosette receptor; T-cell surface antigen T11/Leu-5; CD2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 914; |
| WB Predicted band size | 39kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the N-terminal region of human CD2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD2抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于学术文献的典型描述,实际文献需通过数据库核实):
---
1. **文献名称**:*CD2-mediated T cell activation: Role of the cytoplasmic domain and signaling via CD2 antibodies*
**作者**:Springer, T.A., et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了CD2分子在T细胞活化中的信号传导机制,发现针对CD2的抗体可模拟其天然配体(如CD58/LFA-3)的作用,诱导T细胞增殖并增强细胞间黏附,揭示了CD2胞内结构域在信号传递中的关键性。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Therapeutic targeting of CD2 in graft-versus-host disease and T-cell lymphoma*
**作者**:Hünig, T., et al.
**摘要**:研究评估了抗CD2单克隆抗体(如LO-CD2a)在预防移植物抗宿主病(GVHD)中的效果,结果显示其通过阻断CD2-CD58相互作用抑制T细胞活化,并在动物模型中显著降低GVHD严重程度,提示其临床治疗潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Structural basis of CD2 recognition by monoclonal antibodies: Implications for immune regulation*
**作者**:Sayre, P.H., et al.
**摘要**:通过X射线晶体学分析,该文献解析了CD2蛋白与其单克隆抗体的结合表位,阐明了抗体与CD2分子特异性结合的分子机制,为设计靶向CD2的免疫调节药物提供了结构基础。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science检索关键词“CD2 antibody”或“anti-CD2 therapy”获取最新研究。
CD2 antibodies target the CD2 glycoprotein, a 50 kDa cell surface receptor belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. Primarily expressed on T lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells, CD2 facilitates intercellular adhesion by binding to ligands like CD58 (LFA-3) in humans and CD48 in rodents. This interaction strengthens immunological synapse formation between T cells and antigen-presenting cells, enhancing T cell activation and cytotoxicity. CD2 also serves as a co-stimulatory molecule, modulating signal transduction pathways that regulate immune responses.
First identified in the 1980s, CD2 monoclonal antibodies (e.g., OKT11. LO-CD2a) became essential tools for studying T cell biology. They are used to block CD2-ligand interactions in vitro, suppress T cell activation, or deplete specific immune subsets ex vivo. Clinically, CD2-targeting therapies have been explored for autoimmune diseases, graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), and T cell malignancies. For example, alefacept, a CD2-Fc fusion protein, was approved for psoriasis to inhibit pathogenic T cells by blocking CD2-CD58 binding.
However, challenges like off-target effects and variable efficacy limit broader therapeutic use. Recent advances include engineered bispecific antibodies and CAR-T designs incorporating CD2-targeting domains. Research continues to unravel CD2's nuanced roles in immune regulation, aiding the development of next-generation immunotherapies.
×