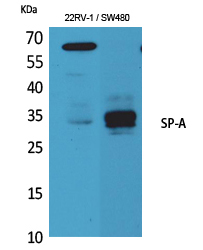
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SFTPA2; COLEC5; PSAP; SFTP1; SFTPA; SFTPA2B; Pulmonary surfactant-associated protein A2; PSP-A; PSPA; SP-A; SP-A2; 35 kDa pulmonary surfactant-associated protein; Alveolar proteinosis protein; Collectin-5; SFTPA1; COLEC4; PSAP; |
| Entrez GeneID | 729238; |
| WB Predicted band size | 34kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human SP-A. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于 **SP-A(Surfactant Protein A)抗体** 的参考文献概要:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Structure and function of surfactant protein A in pulmonary host defense"*
**作者**: McCormack FX, Whitsett JA
**摘要**: 综述了SP-A的分子结构及其在肺部先天免疫中的作用,重点讨论了SP-A抗体在识别病原体和调节肺泡巨噬细胞功能中的应用。
2. **文献名称**: *"Surfactant protein A-deficient mice are susceptible to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection"*
**作者**: Kuroki Y, Tsutahara S, et al.
**摘要**: 通过SP-A基因敲除小鼠模型,发现SP-A缺失导致肺部对细菌感染的易感性增加,并利用SP-A抗体验证其在调理吞噬中的作用。
3. **文献名称**: *"Antibody responses to surfactant protein D and A in patients with COPD"*
**作者**: Mikerov AN, Haque R, et al.
**摘要**: 研究COPD患者血清中SP-A抗体的水平,发现其与疾病严重程度相关,提示SP-A抗体可能作为肺部炎症的生物标志物。
4. **文献名称**: *"Gender differences in murine pulmonary responses to SP-A immunization"*
**作者**: Matalon S, Shagan T, et al.
**摘要**: 比较雌雄动物对SP-A抗体的免疫反应差异,发现雌性小鼠通过SP-A抗体介导更强的抗病毒防御机制,可能与激素调控有关。
---
以上文献涵盖了SP-A抗体的功能研究、疾病关联及临床应用方向,具体可通过PubMed或期刊数据库检索原文。
Surfactant Protein A (SP-A) is a critical component of pulmonary surfactant, primarily produced by alveolar type II cells and Clara cells in the lungs. As a member of the collectin family, SP-A plays a key role in innate immunity, enhancing pathogen opsonization, regulating surfactant homeostasis, and modulating inflammatory responses. SP-A antibodies, though less commonly studied than other autoantibodies, have garnered attention in the context of autoimmune and interstitial lung diseases (ILDs).
In autoimmune disorders like anti-synthetase syndrome (ASS), SP-A antibodies are occasionally detected alongside myositis-specific antibodies (e.g., anti-Jo-1). Their presence is associated with rapidly progressive ILD, suggesting a potential role in disease pathogenesis or as a biomarker for severe pulmonary involvement. However, SP-A antibodies lack high sensitivity compared to other autoantibodies, limiting their diagnostic utility.
Research also links SP-A autoantibodies to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and connective tissue disease-associated ILD, where they may contribute to alveolar epithelial injury and aberrant immune activation. Genetic and environmental factors, such as smoking or occupational exposures, might trigger antibody production by altering SP-A structure or exposure.
Despite these associations, the exact mechanisms of SP-A antibody generation and their functional impact remain unclear. Current clinical applications focus on their utility as adjunct biomarkers in ILD prognosis and stratification. Further studies are needed to clarify their pathogenic significance and therapeutic implications.
×