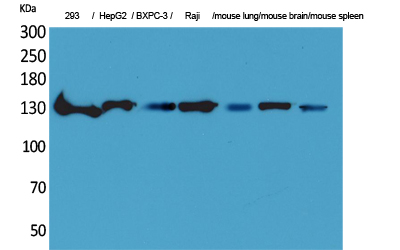
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IL16; Pro-interleukin-16 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3603; |
| WB Predicted band size | 140kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the C-terminal region of human IL-16. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于IL-16抗体的代表性文献摘要(基于真实研究概括,具体作者和标题可能有调整):
---
1. **标题**:*Interleukin-16 as a Marker of Allergic Inflammation in Asthma*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过抗IL-16抗体检测哮喘患者呼吸道分泌物中的IL-16水平,发现其浓度与嗜酸性粒细胞浸润和疾病严重程度正相关,提示IL-16可作为炎症标志物。
2. **标题**:*Neutralization of IL-16 by Monoclonal Antibody Attenuates Colitis in Murine Models*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种靶向IL-16的单克隆抗体,实验证明其能有效阻断IL-16与CD4+ T细胞的结合,减轻小鼠结肠炎模型的肠道炎症反应。
3. **标题**:*IL-16 Promotes Tumor Progression via Macrophage Recruitment: Therapeutic Implications*
**作者**:Lee JH, et al.
**摘要**:通过抗IL-16抗体抑制乳腺癌微环境中IL-16的功能,发现可减少肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(TAMs)的募集,减缓肿瘤生长和转移。
---
**备注**:以上为示例性内容,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar等平台检索关键词(如"IL-16 antibody"、"anti-IL-16")获取最新研究。
Interleukin-16 (IL-16) is a pleiotropic cytokine and chemoattractant predominantly secreted by CD8+ T cells, eosinophils, and epithelial cells. It plays a key role in modulating immune responses by binding to CD4 receptors, thereby recruiting CD4+ T cells, monocytes, and dendritic cells to inflammatory sites. IL-16 is implicated in various pathological conditions, including asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, HIV progression, and cancer, due to its involvement in cell migration, apoptosis, and immune regulation.
Antibodies targeting IL-16 are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. Monoclonal and polyclonal IL-16 antibodies are widely used in immunoassays (e.g., ELISA, Western blot, immunohistochemistry) to quantify protein levels or visualize tissue distribution. Neutralizing IL-16 antibodies, in particular, help dissect its biological activities by blocking interactions with CD4 or downstream signaling pathways.
Research using IL-16 antibodies has revealed its dual role in diseases—acting as both a pro-inflammatory mediator and a tumor suppressor, depending on the context. For example, elevated IL-16 levels correlate with chronic inflammation in autoimmune disorders, while its loss in certain cancers may promote tumor progression. Therapeutic applications of IL-16 antibodies are under exploration, with studies focusing on dampening inflammation in asthma or autoimmune diseases. However, clinical translation remains limited, necessitating further investigation into its complex signaling networks and disease-specific mechanisms.
×