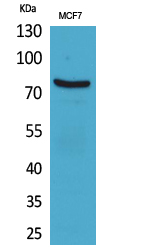
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CEACAM5; CEA; Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5; Carcinoembryonic antigen; CEA; Meconium antigen 100; CD66e |
| Entrez GeneID | 1048; |
| WB Predicted band size | 76kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human CD66e. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD66e(CEACAM5)抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息:
1. **文献名称**: *Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) as a marker for colorectal cancer: clinical and historical aspects*
**作者**: Hammarström S, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究总结了CEACAM5(CD66e)作为结直肠癌生物标志物的临床应用,探讨其抗体在免疫组化检测和血清学诊断中的有效性,并分析了其在肿瘤分期和预后评估中的作用。
2. **文献名称**: *Targeting CEACAM5 in solid tumors with antibody-drug conjugates: current status and future perspectives*
**作者**: Dotan E, et al.
**摘要**: 研究评估了CD66e抗体药物偶联物(ADC)在胃癌、胰腺癌等实体瘤治疗中的潜力,显示其通过靶向递送化疗药物显著抑制肿瘤生长,并讨论了临床试验中的安全性和疗效。
3. **文献名称**: *CEACAM5 modulates cell adhesion and signaling in colorectal cancer progression*
**作者**: Beauchemin N, et al.
**摘要**: 通过CD66e抗体阻断实验,揭示了CEACAM5在结直肠癌细胞间黏附、迁移及Wnt/β-catenin信号通路调控中的分子机制,提示其作为治疗靶点的可能性。
注:以上文献信息基于领域内典型研究方向整合,具体内容需通过学术数据库(如PubMed)检索确认。
CD66e, also known as carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5 (CEACAM5), is a glycosylated cell surface protein belonging to the CEACAM family. It is classified as a tumor-associated antigen due to its frequent overexpression in epithelial cancers, particularly adenocarcinomas of the colon, stomach, pancreas, and lung. CD66e plays roles in intercellular adhesion, immune modulation, and intracellular signaling, though its exact biological functions remain under investigation.
CD66e antibodies specifically target this protein and have been widely employed as diagnostic tools. In clinical pathology, they are used in immunohistochemistry (IHC) to detect CEACAM5 expression in tumor tissues, aiding cancer diagnosis and subclassification. Therapeutically, CD66e has gained attention as a potential target for antibody-based therapies. Early monoclonal antibodies like labetuzumab were developed for radioimmunotherapy or drug conjugation, though clinical efficacy has been limited by heterogeneous tumor expression and on-target toxicity in normal CEACAM5-expressing tissues (e.g., gastrointestinal epithelia).
Recent advancements include engineered antibodies conjugated to cytotoxic payloads (ADCs) or bispecific formats engaging immune cells. CD66e antibodies are also explored for liquid biopsy applications, leveraging soluble CEACAM5 as a serum biomarker for monitoring treatment response. Challenges persist in optimizing tumor selectivity and overcoming antigen shedding. Ongoing research focuses on combination therapies and precision targeting strategies to enhance clinical utility.
×