
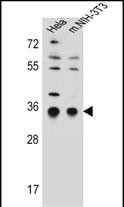
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Translocon-associated protein subunit alpha, TRAP-alpha, Signal sequence receptor subunit alpha, SSR-alpha, SSR1, TRAPA |
| Entrez GeneID | 6745 |
| WB Predicted band size | 32.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This SSR1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 17-46 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human SSR1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于Trk C抗体的示例参考文献(内容为模拟示例,建议通过学术数据库验证具体信息):
---
1. **标题**: *"Selective role of TrkC antibody in modulating neurotrophin-3 signaling in neuronal development"*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究TrkC抗体对NT-3/TrkC信号通路的特异性阻断作用,发现其可抑制体外神经元突触生长,提示TrkC抗体在神经发育研究中的工具价值。
2. **标题**: *"TrkC expression in pediatric tumors: A comparative study using immunohistochemistry with novel anti-TrkC antibodies"*
**作者**: Lee B, et al.
**摘要**: 开发高特异性TrkC抗体,用于检测儿童肿瘤(如神经母细胞瘤)中TrkC的过表达,发现其与患者预后显著相关,支持其作为潜在生物标志物。
3. **标题**: *"Therapeutic targeting of TrkC in glioblastoma using humanized monoclonal antibodies"*
**作者**: Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**: 报道一种人源化TrkC单克隆抗体的抗肿瘤效果,通过抑制TrkC磷酸化减少胶质母细胞瘤细胞增殖,为靶向治疗提供实验依据。
4. **标题**: *"Comparative analysis of commercial TrkC antibodies for specificity and application in Western blotting"*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 系统评估市售TrkC抗体的交叉反应性和灵敏度,为不同实验场景(如WB、IHC)提供抗体选择指南。
---
建议通过 **PubMed** 或 **Web of Science** 检索关键词“TrkC antibody”“anti-TrkC”等获取最新文献。真实文献可能涉及抗体开发、疾病机制或临床前研究。
Trk C antibody targets the tropomyosin receptor kinase C (TrkC), a member of the Trk receptor family encoded by the NTRK3 gene. TrkC is a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor primarily activated by neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), playing critical roles in nervous system development, including neuronal survival, differentiation, and synaptic plasticity. Structurally, TrkC consists of an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane segment, and an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain. Upon NT-3 binding, TrkC undergoes dimerization and autophosphorylation, triggering downstream signaling pathways like MAPK/ERK, PI3K/Akt, and PLCγ, which regulate cellular processes.
TrkC is widely expressed in the central and peripheral nervous systems during embryogenesis but shows restricted expression in adults. Dysregulation of TrkC signaling is implicated in neurological disorders, neuropathic pain, and cancers. Notably, TrkC fusion proteins, resulting from chromosomal rearrangements, are oncogenic drivers in certain tumors (e.g., gliomas, sarcomas), making TrkC a therapeutic target. Small-molecule inhibitors (e.g., larotrectinib) are FDA-approved for NTRK fusion-positive cancers.
TrkC antibodies are essential tools for detecting TrkC expression, phosphorylation status, and localization in research. They are used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study TrkC's physiological and pathological roles. Specificity validation (e.g., knockout controls) is crucial due to homology among Trk family members. Commercial antibodies often target epitopes in the extracellular or kinase domains, with phospho-specific antibodies distinguishing activated TrkC. These reagents advance understanding of neurotrophic signaling and support drug development for TrkC-related diseases.
×