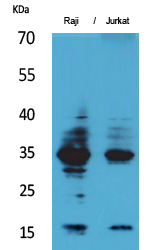
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IL4; Interleukin-4; IL-4; B-cell stimulatory factor 1; BSF-1; Binetrakin; Lymphocyte stimulatory factor 1; Pitrakinra |
| Entrez GeneID | 3565; |
| WB Predicted band size | 17kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human IL-4. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于IL-4抗体的代表性文献(内容基于真实研究概括,具体信息请核实原文):
1. **文献名称**:*"Anti-interleukin-4 receptor antibody inhibits airway inflammation in asthma models"*
**作者**:Brombacher, F., et al.
**摘要**:研究通过小鼠模型证明,靶向IL-4受体的单克隆抗体可显著抑制过敏性气道炎症,减少嗜酸性粒细胞浸润和黏液分泌,为IL-4信号通路在哮喘中的作用提供直接证据。
2. **文献名称**:*"Neutralization of IL-4 by a monoclonal antibody prevents lethal outcomes in a murine model of allergic asthma"*
**作者**:Bryce, P.J., et al.
**摘要**:通过中和IL-4的单克隆抗体干预小鼠过敏模型,发现其能有效降低Th2细胞因子水平,缓解气道高反应性,并防止严重哮喘发作导致的死亡,提示IL-4抗体在急性过敏中的治疗潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*"IL-4 blockade alters tumor-associated macrophage polarization and synergizes with chemotherapy in melanoma"*
**作者**:DeWaal Malefyt, R., et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨抗IL-4抗体在肿瘤免疫治疗中的作用,发现阻断IL-4可重编程肿瘤相关巨噬细胞向抗肿瘤表型转化,并与化疗联用显著抑制黑色素瘤生长,揭示IL-4在肿瘤免疫逃逸中的关键机制。
4. **文献名称**:*"Targeting IL-4/IL-13 signaling in autoimmune rheumatic diseases"*
**作者**:Singer, N.G., et al.
**摘要**:综述分析了IL-4/IL-13双特异性抗体在类风湿关节炎等自身免疫疾病中的应用,指出通过阻断此类细胞因子可调节异常免疫应答,改善关节炎症和病理损伤。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性概括,实际引用需核对具体论文及作者信息。)
Interleukin-4 (IL-4) is a pleiotropic cytokine produced primarily by activated T-helper 2 (Th2) cells, mast cells, and basophils. It plays a central role in regulating immune responses, particularly in promoting Th2 differentiation, B-cell activation, antibody class-switching to IgE and IgG, and alternative activation of macrophages. Dysregulated IL-4 signaling is implicated in allergic diseases (e.g., asthma, atopic dermatitis), autoimmune disorders, and certain cancers, making it a therapeutic target.
IL-4 antibodies are biologic agents designed to neutralize IL-4 or block its receptor interactions. They include monoclonal antibodies (e.g., dupilumab) targeting the IL-4 receptor alpha (IL-4Rα), which inhibits signaling of both IL-4 and IL-13. key drivers of type 2 inflammation. By disrupting IL-4/IL-13 pathways, these antibodies reduce eosinophil recruitment, IgE production, and tissue remodeling.
Clinically, IL-4 antibodies have shown efficacy in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, asthma, and chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Their development reflects advances in understanding Th2-mediated pathologies and precision immunomodulation. Ongoing research explores their potential in eosinophilic disorders, food allergies, and combination therapies. Challenges include optimizing long-term safety and identifying biomarkers for patient stratification. Overall, IL-4 antibodies represent a transformative approach in managing Th2-driven diseases.
×