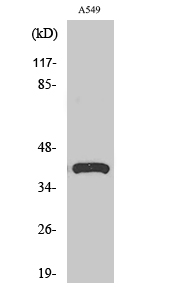
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SFTPB; SFTP3; Pulmonary surfactant-associated protein B; SP-B; 18 kDa pulmonary-surfactant protein; 6 kDa protein; Pulmonary surfactant-associated proteolipid SPL(Phe) |
| Entrez GeneID | 6439; |
| WB Predicted band size | 42kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human SP-B. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SP-B抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要的简要概括:
1. **《Autoantibodies to surfactant protein-B in idiopathic interstitial pneumonias》**
*作者:Kuroki Y, Tsutahara S, Shijubo N, et al.*
**摘要**:该研究检测了特发性间质性肺炎(如IPF和NSIP)患者血清中的SP-B自身抗体,发现其存在可能与疾病活动性和肺泡损伤相关,提示其作为潜在生物标志物的价值。
2. **《Mutations in the surfactant protein B gene associated with hereditary pulmonary disease》**
*作者:Nogee LM, deMello DE, Dehner LP, Colten HR.*
**摘要**:首次报道了SP-B基因突变导致遗传性SP-B缺乏症,引发新生儿严重呼吸衰竭,并探讨了通过抗体检测和基因分析进行早期诊断的方法。
3. **《Surfactant protein-B degradation by alveolar macrophages in acute respiratory distress syndrome》**
*作者:Günther A, Schmidt R, Feustel A, et al.*
**摘要**:研究发现ARDS患者肺泡灌洗液中SP-B水平显著降低,且SP-B抗体可能用于评估肺泡表面活性物质破坏程度及疾病严重性。
4. **《Standardized detection of anti-surfactant protein B antibodies in neonatal screening》**
*作者:Brasch F, Griese M, Tredano M, et al.*
**摘要**:开发了一种基于ELISA的标准化方法检测新生儿血清中SP-B抗体,用于早期识别遗传性或获得性SP-B功能障碍相关疾病。
这些文献涵盖了SP-B抗体在疾病机制、诊断及临床应用中的不同研究方向。
Surfactant protein B (SP-B) is a critical component of pulmonary surfactant, a lipid-protein complex essential for reducing alveolar surface tension and maintaining respiratory function. SP-B, encoded by the *SFTPB* gene, is synthesized by alveolar type II cells and promotes surfactant monolayer stability during breathing cycles. Deficiencies in SP-B, often due to autosomal recessive mutations, are linked to severe neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (NRDS) and interstitial lung diseases.
Anti-SP-B antibodies are primarily used in research and diagnostics to detect SP-B expression in lung tissues or surfactant samples. Immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and ELISA are common techniques employing these antibodies to study surfactant metabolism, alveolar development, or genetic disorders. In clinical contexts, autoantibodies against SP-B have been reported in rare cases of autoimmune-related interstitial lung diseases, though their pathogenic role remains unclear. Commercially available SP-B antibodies are typically monoclonal or polyclonal, targeting specific epitopes for precise detection. Recent studies also explore SP-B as a biomarker for lung injury or therapeutic response monitoring. However, cross-reactivity with other surfactant proteins (e.g., SP-C) requires careful validation in experimental setups. Understanding SP-B antibody interactions aids in elucidating surfactant dysfunction mechanisms and developing targeted therapies for respiratory pathologies.
×