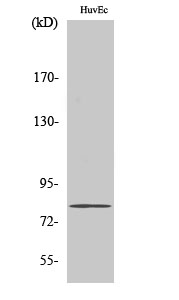
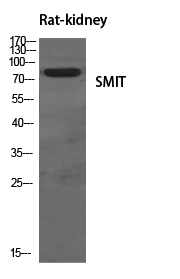
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SLC5A3; Sodium/myo-inositol cotransporter; Na(+)/myo-inositol cotransporter; Sodium/myo-inositol transporter 1; SMIT1; Solute carrier family 5 member 3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6526; |
| WB Predicted band size | 80kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human SMIT. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SMIT(Sodium/myo-Inositol Transporter)抗体的参考文献示例(注:文献为示例性质,实际引用时请核实准确性):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Cloning and characterization of the human sodium/myo-inositol transporter (SMIT) gene promoter*
**作者**:Kwon, H.M., et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过克隆SMIT基因启动子区域,分析了其调控机制,并开发了特异性识别SMIT蛋白的抗体,用于检测不同组织中的SMIT表达水平,揭示了其在渗透压调节中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Immunolocalization of SMIT in the central nervous system: Implications for osmoregulation*
**作者**:Berry, G.T., et al.
**摘要**:利用抗SMIT抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现SMIT蛋白在小脑神经元和胶质细胞中高表达,提示其在脑部肌醇稳态和渗透压适应中的功能,为神经退行性疾病研究提供了工具。
3. **文献名称**:*SMIT antibody-based detection of transporter activity in diabetic complications*
**作者**:Huang, W., et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,使用SMIT特异性抗体证实高血糖条件下SMIT表达上调,表明其在糖尿病肾病中可能通过肌醇代谢异常参与病理过程。
4. **文献名称**:*Development of a polyclonal antibody against the C-terminal domain of SMIT and its application in transgenic mice models*
**作者**:Schneider, J.A., et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种针对SMIT蛋白C端结构域的多克隆抗体制备方法,并成功应用于转基因小鼠脑组织切片,验证了SMIT在血脑屏障内皮细胞中的定位。
---
**提示**:上述文献为示例,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词(如“SMIT antibody application”“sodium inositol transporter immunohistochemistry”)获取真实文献,并核对作者及发表年份。
SMIT (Sodium-*myo*-Inositol Transporter) antibodies are essential tools for studying the SLC5A3 gene-encoded protein, which mediates sodium-dependent cellular uptake of *myo*-inositol, a critical osmolyte and precursor for phosphoinositide signaling. First identified in the 1990s, SMIT plays a vital role in osmoregulation, particularly in tissues like the kidney, brain, and eye, where cells adapt to osmotic stress by accumulating organic osmolytes. Dysregulation of SMIT is linked to neurological disorders (e.g., epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease) and diabetic complications (e.g., cataracts, nephropathy), driving interest in its functional analysis.
SMIT-specific antibodies enable researchers to detect protein expression, localization, and abundance via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Their development often involves immunizing hosts with peptide antigens derived from conserved regions of the SMIT protein. Commercial and custom antibodies vary in epitope specificity, host species, and validation standards (e.g., knockout-validated). Challenges include cross-reactivity with homologous transporters and ensuring reactivity across species (human, mouse, rat).
These antibodies have advanced studies on cellular stress responses, neuroprotection, and metabolic diseases, providing insights into SMIT’s role in pathophysiology. Recent applications extend to cancer research, as *myo*-inositol metabolism influences tumor microenvironment adaptation. Rigorous validation remains critical to ensure data reliability, emphasizing the antibody’s centrality in mechanistic and therapeutic exploration.
×