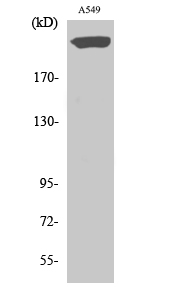
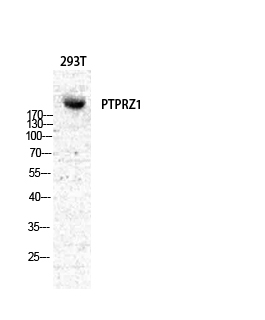
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PTPRZ1; HTPZP2; PTPRZ; PTPRZ2; PTPZ; Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase zeta; R-PTP-zeta; Protein-tyrosine phosphatase receptor type Z polypeptide 1; Protein-tyrosine phosphatase receptor type Z polypeptide 2; R-PTP-zeta-2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5803; |
| WB Predicted band size | 250kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the N-terminal region of human PTPζ. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于 **PTPζ抗体** 的参考文献概览,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容简述:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase ζ (PTPRZ) regulates oligodendrocyte precursor cell differentiation through extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling"*
**作者**:Kuboyama K. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用特异性PTPζ抗体,发现其通过调控ERK信号通路影响少突胶质前体细胞的分化,揭示了PTPζ在中枢神经系统髓鞘形成中的作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Monoclonal antibody targeting the extracellular domain of PTPRZ inhibits glioma growth"*
**作者**:Umemori H. et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种靶向PTPζ胞外结构域的单克隆抗体,实验显示其可通过阻断配体(如pleiotrophin)结合抑制胶质瘤细胞的增殖和迁移。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Phosphatase activity of receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase ζ (PTPRZ) is essential for neurite outgrowth"*
**作者**:Niisato K. et al.
**摘要**:通过PTPζ抗体阻断实验,证明其磷酸酶活性对神经元轴突延伸至关重要,提示其在神经发育和再生中的潜在应用。
---
4. **文献名称**:*"Expression of PTPRZ1 in glioblastoma and its role in tumor cell invasion"*
**作者**:Foehr E.D. et al.
**摘要**:利用免疫组化(PTPζ抗体)分析发现PTPRZ1在胶质母细胞瘤中高表达,并通过调控细胞黏附和基质降解促进肿瘤侵袭。
---
以上文献均聚焦于PTPζ抗体的应用,涵盖神经发育、肿瘤治疗等领域。如需具体文献来源或DOI,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science进一步检索。
**Background of PTPζ Antibodies**
PTPζ (Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Zeta), also known as RPTPβ or PTPRZ, is a receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase predominantly expressed in the central nervous system (CNS). It plays critical roles in neural development, glioblastoma progression, and neuronal regeneration. Structurally, PTPζ consists of an extracellular carbonic anhydrase-like domain, fibronectin type III repeats, and intracellular tyrosine phosphatase domains, enabling its involvement in cell adhesion, migration, and signal transduction.
Antibodies targeting PTPζ are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation to investigate PTPζ's role in neural stem cell regulation, oligodendrocyte differentiation, and interactions with ligands such as pleiotrophin (PTN) and IL-34. Research has highlighted PTPζ's dual role in both promoting and suppressing tumor growth, depending on cellular context, making it a potential therapeutic target in glioblastoma.
Additionally, PTPζ antibodies aid in exploring its involvement in neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s) and psychiatric disorders, where disrupted signaling pathways may contribute to pathology. Variants like PTPζ-A (full-length transmembrane form) and phosphacan (secreted isoform) are often distinguished using isoform-specific antibodies. Ongoing studies focus on elucidating PTPζ's phosphatase-dependent and -independent mechanisms, underscoring its significance in CNS biology and disease.
×