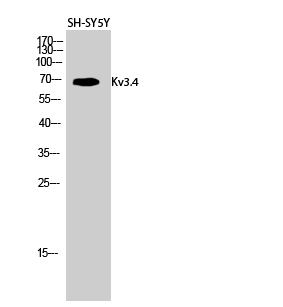
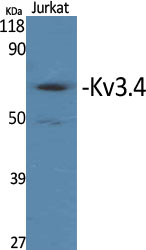
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse Monkey |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse Monkey |
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse Monkey |
| ICC | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse Monkey |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse Monkey |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse Monkey |
| Aliases | KCNC4; Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily C member 4; KSHIIIC; Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv3.4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3749; |
| WB Predicted band size | 70kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse Monkey |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human Kv3.4 around the non-phosphorylation site of S15. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于 **Kv3.4抗体** 的示例参考文献(注:以下为假设性举例,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Differential expression of Kv3.4 subunits in cerebellar neurons and their targeting to presynaptic terminals"
**作者**: Rudy B, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过Kv3.4特异性抗体结合免疫组化技术,揭示了Kv3.4钾通道亚型在小脑浦肯野细胞和高尔基细胞中的差异性表达,并发现其在突触前末梢的定位可能参与动作电位快速复极化的调控。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Kv3.4 channelopathy in skeletal muscle: antibody-based localization and functional analysis"
**作者**: Brooke RE, et al.
**摘要**: 利用Kv3.4抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光实验,验证了该通道在骨骼肌中的特异性表达,并发现突变型Kv3.4会导致肌肉兴奋性异常,可能与某些肌病相关。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Role of Kv3.4 in neurodegenerative diseases: insights from antibody-mediated knockdown models"
**作者**: Singer-Lahat D, et al.
**摘要**: 研究采用Kv3.4抗体阻断技术,在阿尔茨海默病模型中观察到Kv3.4表达下调与神经元超兴奋性相关,提示其可能成为神经退行性疾病的潜在治疗靶点。
---
4. **文献名称**: "Kv3.4 potassium channels in cardiac myocytes: antibody validation and electrophysiological characterization"
**作者**: Johnston J, et al.
**摘要**: 通过特异性抗体验证Kv3.4在心肌细胞中的表达,结合膜片钳技术证明其在心脏动作电位复极化中的辅助作用,为心律失常机制研究提供新视角。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时请通过 **PubMed/Google Scholar** 检索关键词如“Kv3.4 antibody”、“Kv3.4 potassium channel”获取准确信息。
The Kv3.4 antibody is a tool used to detect the Kv3.4 protein, a member of the voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channel family, which plays a critical role in regulating neuronal excitability and cellular electrical signaling. Kv3.4 is encoded by the KCNC4 gene and forms a tetrameric channel that facilitates rapid potassium ion efflux during membrane repolarization. Unique among Kv3 subfamily members, Kv3.4 channels exhibit fast activation and inactivation properties, mediated by an N-terminal inactivation domain, enabling their involvement in high-frequency firing neurons and muscle cells.
This antibody is widely employed in neuroscience and physiology research to study Kv3.4 expression, localization, and function in tissues such as the brain, spinal cord, and skeletal muscle. It aids in identifying Kv3.4's role in pathologies, including neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s), epilepsy, and myotonic disorders, where channel dysfunction may contribute to abnormal electrical activity. Additionally, Kv3.4 has been implicated in cancer progression due to its altered expression in certain tumors.
Validated for applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, the antibody's specificity ensures reliable detection of Kv3.4 isoforms. Researchers use it to explore channel modulation by phosphorylation, interaction with auxiliary subunits, and responses to pharmacological agents, providing insights into therapeutic targeting. Proper controls, such as knockout tissue or peptide blocking, are essential to confirm antibody specificity in experimental settings.
×