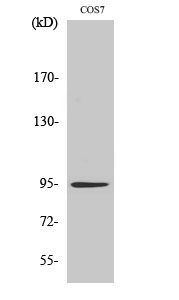
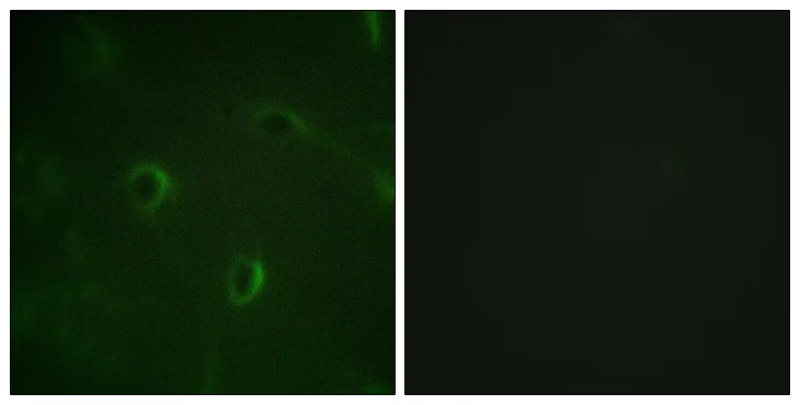
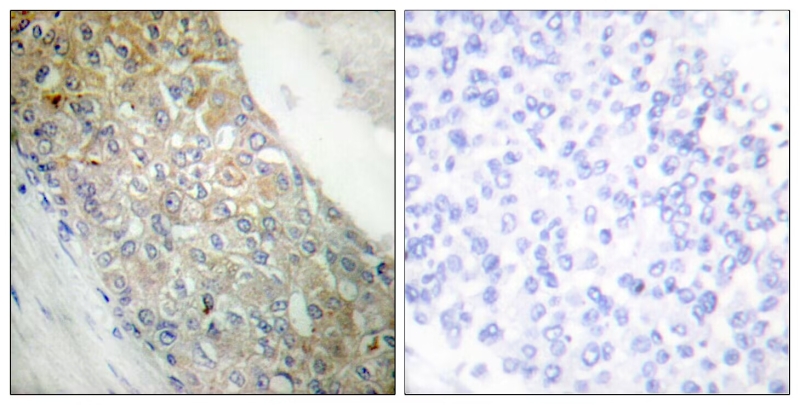
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat Monkey |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat Monkey |
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat Monkey |
| ICC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat Monkey |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat Monkey |
| Elisa | 1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat Monkey |
| Aliases | INSR; Insulin receptor; IR; CD antigen CD220 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3643; |
| WB Predicted band size | 95kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat Monkey |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human Insulin R around the non-phosphorylation site of Y1361. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与胰岛素受体抗体(Insulin Receptor Antibodies, IRAs)相关的经典文献摘要,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Syndromes of Severe Insulin Resistance and/or Lipodystrophy: Clinical Course, Metabolic Features, and Effects of Treatment"*
**作者**: Arioglu E, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究描述了B型胰岛素抵抗综合征患者体内胰岛素受体自身抗体的作用,指出这些抗体会阻断受体功能,导致严重的高血糖和胰岛素抵抗,部分患者可能伴随其他自身免疫疾病。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"The Syndrome of Autoantibodies to the Insulin Receptor: Clinical Features and Mechanistic Insights"*
**作者**: Kahn CR, et al.
**摘要**: 早期研究中首次报道了针对胰岛素受体的自身抗体(IRAs),揭示了其通过阻断胰岛素信号或异常激活受体两种机制,导致糖尿病或低血糖等矛盾代谢表型。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Structural Basis of Insulin Receptor Activation by Antibodies"*
**作者**: Taylor SI, et al.
**摘要**: 通过结构生物学方法解析胰岛素受体与不同抗体的相互作用,发现部分抗体可模拟胰岛素效应激活受体,而另一些则抑制其功能,为靶向治疗提供理论依据。
---
**备注**:上述文献可通过PubMed或Sci-Hub获取全文。若需具体年份或补充文献,可进一步说明研究方向(如临床案例、分子机制等)。
Insulin receptor (IR) antibodies are specialized immunoglobulins that target the insulin receptor, a transmembrane protein critical for glucose homeostasis. The insulin receptor consists of two extracellular α-subunits that bind insulin and two β-subunits with tyrosine kinase activity, enabling downstream signaling upon ligand activation. IR antibodies can act as either antagonists or agonists, depending on their binding epitopes and mechanisms. Antagonistic antibodies block insulin binding, impairing receptor activation and leading to insulin resistance, a hallmark of type 2 diabetes and rare conditions like type B insulin resistance syndrome. In contrast, agonistic antibodies mimic insulin by triggering receptor autophosphorylation and signaling, which may cause hypoglycemia, as seen in autoimmune hypoglycemia syndromes.
These antibodies are primarily used in research to study insulin signaling pathways, receptor structure-function relationships, and metabolic disorders. Monoclonal IR antibodies, generated via hybridoma or recombinant technologies, are valuable tools for immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and receptor inhibition assays. Clinically, detecting endogenous IR autoantibodies aids in diagnosing autoimmune metabolic diseases. However, their pathogenic role in disorders such as severe insulin resistance or hypoglycemia underscores their dual nature as both research tools and disease biomarkers. Understanding IR antibody interactions continues to inform therapeutic strategies for diabetes and metabolic syndromes.
×