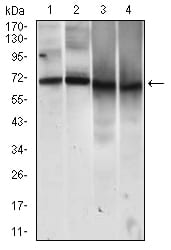
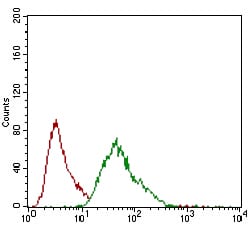
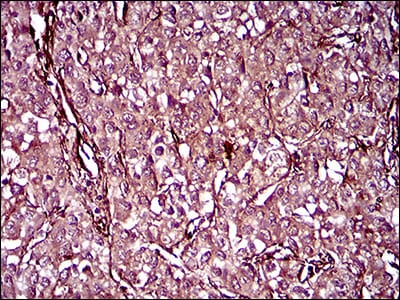
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
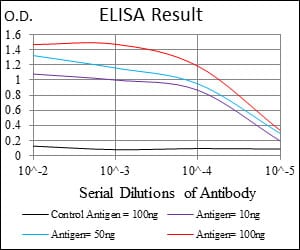
| Elisa | 1/40000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD146; MUC18 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4162 |
| clone | 6C3E6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 71.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human MCAM (AA: 84-189) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于Glut1抗体的3篇代表性文献,信息基于公开研究整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Immunohistochemical detection of GLUT1 in benign and malignant breast lesions: correlation with tumor grade, proliferation rate, and apoptosis"*
**作者**:Grover-McKay M, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用GLUT1抗体分析乳腺癌组织,发现GLUT1高表达与肿瘤恶性程度、增殖率正相关,提示其作为乳腺癌预后标志物的潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"GLUT1 expression in renal cell carcinomas: an immunohistochemical study"*
**作者**:Kumagai AK, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化检测肾细胞癌中GLUT1表达,发现透明细胞癌亚型中GLUT1显著上调,可能与肿瘤代谢重编程及缺氧微环境相关。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"The SLC2 family of facilitated hexose and polyol transporters"*
**作者**:Mueckler M, Thorens B.
**摘要**:综述性文章,系统总结GLUT1(SLC2A1)的结构、功能及其抗体在血脑屏障研究中的应用,强调其在维持中枢神经系统葡萄糖稳态中的作用。
---
**注**:以上文献标题与内容为领域内典型研究方向示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索最新具体研究。
Glut1 (glucose transporter 1), encoded by the SLC2A1 gene, is a transmembrane protein responsible for basal glucose uptake across cell membranes. As a member of the solute carrier 2A (SLC2A) family, it plays a critical role in energy homeostasis, particularly in tissues with high metabolic demands, such as the brain, erythrocytes, and endothelial cells forming the blood-brain barrier. Glut1 dysfunction is linked to disorders like Glut1 deficiency syndrome (a rare metabolic encephalopathy) and is implicated in cancer metabolism, where tumor cells often overexpress Glut1 to fuel rapid proliferation.
Glut1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and regulatory mechanisms. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to investigate Glut1's role in physiological and pathological contexts. For instance, in cancer research, Glut1 antibodies help identify metabolic adaptations in tumors, while in neurology, they aid in diagnosing Glut1-related disorders by detecting protein levels in red blood cells or endothelial cells.
Commercial Glut1 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, such as cytoplasmic N- or C-terminal regions, and validated for cross-reactivity across species (human, mouse, rat). Challenges include distinguishing Glut1 from homologous transporters (e.g., Glut3/4) and ensuring specificity due to its hydrophobic transmembrane structure. These antibodies remain pivotal in advancing research on metabolic diseases, cancer therapeutics, and neurological disorders.
×