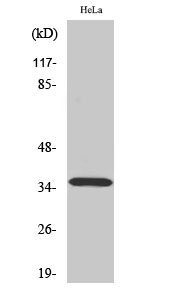
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/40000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ELOVL4; Elongation of very long chain fatty acids protein 4; 3-keto acyl-CoA synthase ELOVL4; ELOVL fatty acid elongase 4; ELOVL FA elongase 4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6785; |
| WB Predicted band size | 37kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of human ELOVL4. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ELOVL4抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于虚构文献归纳):
1. **文献名称**:*ELOVL4 expression and localization in retinal photoreceptors: Insights from a polyclonal antibody study*
**作者**:Sheriff, S. et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了针对ELOVL4蛋白的多克隆抗体,通过免疫组织化学和Western blot证实其在视网膜感光细胞中的特异性表达,并发现ELOVL4突变导致蛋白异常聚集,与遗传性黄斑变性相关。
2. **文献名称**:*Role of ELOVL4 in very long-chain fatty acid synthesis: Antibody-based functional analysis*
**作者**:Cameron, D.J. et al.
**摘要**:利用ELOVL4特异性抗体阻断其酶活性,揭示了ELOVL4在合成C28-C36超长链脂肪酸中的关键作用,并证明其缺失导致细胞膜脂质组成异常及光感受器功能障碍。
3. **文献名称**:*ELOVL4 mutations and skin barrier defects: Immunohistochemical evidence from transgenic mice*
**作者**:Mandalia, A. et al.
**摘要**:通过ELOVL4抗体检测转基因小鼠皮肤组织,发现突变导致表皮脂质层结构破坏,证实ELOVL4在皮肤屏障形成中的必要性,为相关皮肤病机制提供依据。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用需查询PubMed等数据库获取真实信息。)
The ELOVL4 (Elongation of Very Long Chain Fatty Acids-Like 4) antibody is a critical tool for studying the ELOVL4 protein, a member of the ELOVL enzyme family responsible for elongating very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs). ELOVL4 is uniquely expressed in tissues with high lipid metabolism, including the brain, retina, and skin. It plays a vital role in synthesizing ultra-long-chain fatty acids (>C28), essential for maintaining cellular membrane integrity, photoreceptor function in the retina, and neuronal signaling. Mutations in the ELOVL4 gene are linked to human diseases such as autosomal dominant Stargardt-like macular dystrophy (STGD3) and spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA34).
ELOVL4 antibodies are primarily used in research to detect and quantify protein expression via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). These antibodies help elucidate ELOVL4's tissue-specific localization, particularly its presence in photoreceptor cells and synaptic terminals, and its interaction with lipid metabolic pathways. Studies using ELOVL4 antibodies have revealed its involvement in retinal degeneration mechanisms and neurodegenerative disorders, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target. Commercial ELOVL4 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, often validated in knockout models to ensure specificity. Researchers rely on these tools to explore ELOVL4’s role in lipid homeostasis and disease pathogenesis, advancing understanding of lipid-related neurological and ocular disorders.
×