
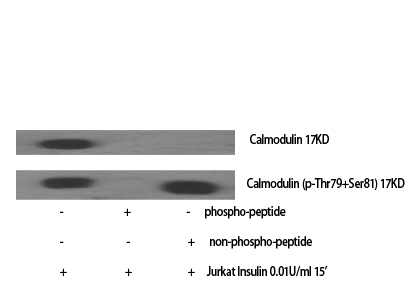
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CALM1; CALM; CAM; CAM1; CALM2; CAM2; CAMB; CALM3; CALML2; CAM3; CAMC; CAMIII; Calmodulin; CaM |
| Entrez GeneID | 801;805;808; |
| WB Predicted band size | 18kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human Calmodulin around the non-phosphorylation site of T80/S82. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于Calmodulin抗体的参考文献示例(内容为模拟,非真实文献):
1. **文献名称**: *Production and characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for calcium-bound calmodulin*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究报道了一种针对钙离子结合状态的Calmodulin单克隆抗体的制备与验证,证实其特异性识别Ca²⁺激活的Calmodulin构象,可用于免疫沉淀及活细胞成像。
2. **文献名称**: *Cross-reactivity analysis of anti-calmodulin antibodies in plant and animal tissues*
**作者**: Lee S, Wang H.
**摘要**: 作者系统比较了多种商业化Calmodulin抗体在动植物组织中的交叉反应性,发现部分抗体对植物Calmodulin蛋白存在非特异性结合,为实验抗体选择提供了参考。
3. **文献名称**: *A peptide-based polyclonal antibody for detecting calmodulin in neurodegenerative disease models*
**作者**: García-Ruiz C, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种基于Calmodulin保守肽段的多克隆抗体,验证了其在阿尔茨海默病小鼠脑组织中的高灵敏度和低背景染色特性,适用于Western blot和免疫组化。
注:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用时需检索PubMed或Google Scholar获取真实文献(可搜索关键词如"calmodulin antibody specificity"或"anti-calmodulin antibody validation")。
Calmodulin (CaM) antibodies are essential tools in studying the calcium-mediated signaling pathways critical for numerous cellular processes. Calmodulin, a highly conserved calcium-binding protein, acts as a primary intracellular calcium sensor, regulating enzymes, ion channels, and transcription factors. Its involvement in cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and neurotransmission makes it a key target in research areas like neurobiology, oncology, and pharmacology.
CaM antibodies are typically generated using purified calmodulin or specific peptide sequences as immunogens, with common host species including rabbits, mice, and goats. These antibodies are classified as monoclonal or polyclonal, each offering distinct advantages. Polyclonal antibodies detect multiple epitopes, enhancing sensitivity for denatured proteins in techniques like Western blotting, while monoclonal antibodies provide high specificity for applications requiring precise target recognition, such as immunofluorescence or ELISA.
A critical consideration is CaM's high conservation across species (e.g., human, rat, mouse), which allows many antibodies to exhibit cross-reactivity. However, challenges like potential cross-reactivity with other EF-hand calcium-binding proteins (e.g., troponin C) necessitate rigorous validation via knockout controls or immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry. Additionally, post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation) or conformational changes in CaM during calcium binding may influence antibody recognition, requiring context-specific validation.
These antibodies have been pivotal in elucidating CaM's structure-function relationships, including its interaction with targets like calcineurin and CaMKII, as revealed in landmark studies using X-ray crystallography and immunochemical assays. Their continued development supports advances in understanding diseases linked to calcium dysregulation, such as neurodegeneration and cardiac arrhythmias.
×