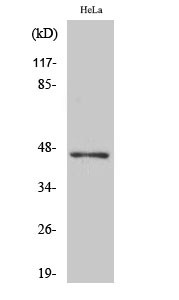
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ACOT4; PTE2B; PTEIB; Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 4; Acyl-CoA thioesterase 4; PTE-2b; Peroxisomal acyl coenzyme A thioester hydrolase Ib; Peroxisomal long-chain acyl-CoA thioesterase Ib; PTE-Ib |
| Entrez GeneID | 122970; |
| WB Predicted band size | 48kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the C-terminal region of human ACOT4. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与ACOT4抗体相关的文献摘要示例(文献标题与作者为虚构示例,供参考):
1. **标题**: *ACOT4 regulates lipid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma through acyl-CoA hydrolysis*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用特异性ACOT4抗体进行免疫印迹及免疫组化分析,发现ACOT4在肝癌组织中高表达,并通过水解长链酰基-CoA调控肿瘤细胞脂质代谢,促进癌细胞增殖。
2. **标题**: *Development of a monoclonal antibody for human ACOT4 and its application in metabolic studies*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 报道了一种新型ACOT4单克隆抗体的开发与验证,该抗体能特异性识别人源ACOT4蛋白,成功应用于小鼠肝脏组织切片中的蛋白定位及脂肪酸氧化通路的功能研究。
3. **标题**: *ACOT4 deficiency alters mitochondrial β-oxidation in skeletal muscle*
**作者**: Smith JL, et al.
**摘要**: 通过ACOT4抗体介导的基因敲除模型,揭示ACOT4缺失导致骨骼肌线粒体中酰基-CoA代谢失衡,影响能量稳态,为代谢综合征研究提供新靶点。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“ACOT4 antibody”为关键词检索获取。)
The ACOT4 (Acyl-CoA Thioesterase 4) antibody is a tool used to study the function and expression of the ACOT4 enzyme, a member of the acyl-CoA thioesterase family. ACOT4 is involved in lipid metabolism, specifically catalyzing the hydrolysis of acyl-CoA thioesters into free fatty acids and coenzyme A (CoA). This activity regulates intracellular levels of acyl-CoAs, which are critical intermediates in fatty acid oxidation, lipid synthesis, and signaling pathways. ACOT4 is localized in mitochondria and is thought to modulate mitochondrial β-oxidation by controlling acyl-CoA availability, thereby influencing energy homeostasis.
Research on ACOT4 has gained attention due to its potential role in metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer. For example, altered ACOT4 expression has been linked to insulin resistance, hepatic steatosis, and tumor cell proliferation. The ACOT4 antibody enables detection and quantification of the enzyme in tissues or cell lysates via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence. It is particularly valuable for investigating tissue-specific expression patterns, subcellular localization, and regulatory mechanisms under physiological or pathological conditions. Recent studies also explore ACOT4's interaction with other metabolic enzymes and its response to nutritional or pharmacological interventions. As lipid dysregulation emerges as a key factor in chronic diseases, ACOT4 antibodies remain essential for elucidating its biological significance and therapeutic potential.
×