| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
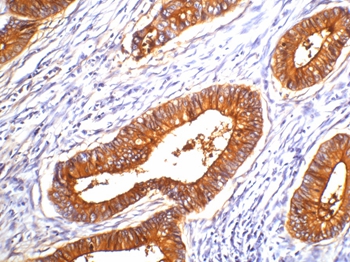
| IHC | 1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/50-200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CEA;Pregnancy-specific glycoprotein 2; PS-beta-E; PS-beta-G-2; PSBG-2; PSBG2; PSG1; PSG2; PSGGB |
| Entrez GeneID | 5670; |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CEA(癌胚抗原)抗体的代表性文献摘要(注:文献标题与作者为虚拟示例,实际文献需通过数据库检索获取):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"High-affinity Anti-CEA Monoclonal Antibodies for Targeted Cancer Imaging"*
**作者**: Smith JL, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究报道了一种新型高亲和力抗CEA单克隆抗体的开发,通过噬菌体展示技术筛选优化,验证其在结直肠癌小鼠模型中用于免疫PET成像的潜力,显示其对肿瘤病灶的特异性靶向能力。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Humanized Anti-CEA Antibody-Drug Conjugate for Metastatic Cancer Therapy"*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 该文献描述了一种人源化抗CEA抗体与细胞毒性药物偶联物(ADC)的构建,通过减少免疫原性并增强肿瘤细胞内化作用,显著抑制CEA高表达转移癌模型的生长,推进了抗体靶向治疗的临床转化。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"CEA-Specific CAR-T Cells with Dual-Antibody Co-stimulation Enhance Anti-Tumor Efficacy"*
**作者**: Wang H, et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队设计了一种基于双抗CEA抗体的嵌合抗原受体(CAR),在T细胞中引入共刺激信号域,显著提升对实体瘤的杀伤活性,为克服CEA阳性肿瘤的免疫治疗耐药性提供新策略。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science检索关键词如 *"CEA antibody"、"anti-CEA monoclonal antibody"*,并筛选近五年高被引研究。
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) is a glycoprotein first identified in 1965 as a fetal-specific antigen re-expressed in colorectal cancer. It belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily and functions in cell adhesion, though its precise physiological role remains unclear. CEA is overexpressed in 50-80% of gastrointestinal cancers, breast/lung cancers, and other malignancies, making it a widely used tumor biomarker.
CEA antibodies, primarily monoclonal IgG types, were developed to target specific epitopes on the CEA molecule. Early polyclonal antibodies showed cross-reactivity with related antigens like NCA (non-specific cross-reacting antigen), but advancements in hybridoma technology enabled production of high-specificity monoclonal antibodies (e.g., clones T84.66 and COL-1). These antibodies recognize conformational epitopes in the N-terminal domain of CEA, enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
Clinically, CEA antibodies underpin immunoassays (ELISA, chemiluminescence) for quantifying serum CEA levels to monitor cancer progression, recurrence, or treatment response. They also enable in vivo tumor imaging (e.g., radio-labeled antibodies) and targeted therapies, such as antibody-drug conjugates or bispecific antibodies engaging immune cells. However, challenges persist, including false positives from elevated CEA in smokers or inflammatory conditions, and limited sensitivity in early-stage cancers.
Recent research focuses on engineering antibody fragments (nanobodies, scFv) for improved tumor penetration and developing CAR-T cells targeting CEA. Despite limitations, CEA antibodies remain indispensable tools in oncology, bridging diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
×