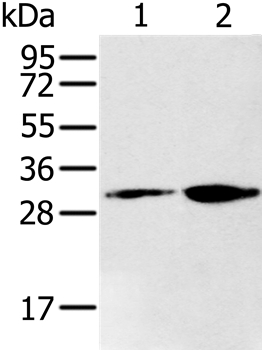
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | C10orf59; RENALASE |
| Entrez GeneID | 55328; |
| WB Predicted band size | 38kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide corresponding to a region derived from internal residues of human renalase, FAD-dependent amine oxidase |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于RNLS(Renalase)抗体的3篇代表性文献,简要整理如下:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Renalase is a novel renal hormone that regulates blood pressure and cardiovascular function*
**作者**:Desir GV, et al.
**摘要**:
该研究首次报道了Renalase作为一种新型肾脏分泌酶的功能,揭示了其通过代谢循环儿茶酚胺调控血压的机制。研究团队开发了特异性抗体,证实其在心血管疾病模型中的表达变化,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Monoclonal Antibody-Based ELISA for Renalase Quantification: Clinical Correlations in Chronic Kidney Disease*
**作者**:Wu Y, et al.
**摘要**:
研究者开发了一种基于单克隆抗体的ELISA检测方法,用于定量人血清中的Renalase水平。通过慢性肾病患者样本验证,发现Renalase浓度与肾功能损伤程度呈负相关,支持其作为生物标志物的临床应用价值。
3. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies Against Renalase in Autoimmune Diseases: Implications for Systemic Inflammation*
**作者**:Li X, et al.
**摘要**:
该研究发现类风湿性关节炎和系统性红斑狼疮患者中存在抗Renalase自身抗体,这些抗体可能通过干扰Renalase的抗氧化功能加剧炎症反应,为自身免疫疾病的机制研究提供了新视角。
---
**备注**:RNLS(Renalase)相关研究多聚焦于其在心血管、肾脏疾病及代谢调控中的作用,上述文献反映了抗体在基础机制探索、诊断技术开发及病理机制研究中的应用。如需具体文献DOI或补充领域,可进一步说明。
RNLS (Renalase), also known as MAO-C, is a flavoprotein first identified in 2005 as a secreted enzyme primarily synthesized in the kidney, liver, and cardiovascular tissues. It plays a critical role in metabolizing catecholamines, such as adrenaline and noradrenaline, thereby regulating blood pressure and cardiovascular homeostasis. Structurally, RNLS contains a conserved FAD-binding domain and exists in multiple isoforms due to alternative splicing. Beyond its enzymatic function, RNLS has emerged as a key modulator of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis, with implications in chronic kidney disease, hypertension, heart failure, diabetes, and cancer.
RNLS antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying RNLS expression in research and diagnostics. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies target specific epitopes, enabling applications in Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA. Elevated RNLS levels in plasma or tissues are associated with disease progression, making it a potential biomarker. Therapeutic RNLS-neutralizing antibodies are under investigation for conditions like cancer, where RNLS promotes tumor growth and metastasis via signaling pathways (e.g., PI3K/AKT). Conversely, recombinant RNLS or agonist antibodies are explored for treating ischemic injury by enhancing cytoprotective pathways. Ongoing studies aim to clarify RNLS' pleiotropic roles and optimize antibody-based interventions.
×