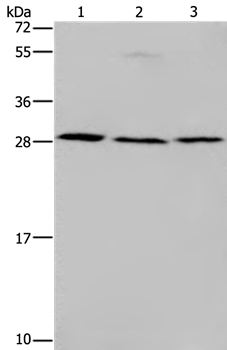
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SIP; Teap; p53DINP1; TP53DINP1; TP53INP1A; TP53INP1B |
| Entrez GeneID | 94241; |
| WB Predicted band size | 27kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide corresponding to residues near the N terminal of human tumor protein p53 inducible nuclear protein 1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于TP53INP1抗体的3篇参考文献,简要概括研究内容:
1. **文献名称**:*TP53INP1 modulates apoptosis through autophagy in pancreatic β-cells*
**作者**:Seillier et al.
**摘要**:研究利用TP53INP1特异性抗体(Western blot和免疫荧光),揭示了该蛋白通过调控自噬影响胰岛β细胞凋亡的机制,为糖尿病病理提供新见解。
2. **文献名称**:*TP53INP1 acts as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer by regulating p53 stability*
**作者**:Jiang et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化(使用TP53INP1抗体)分析结直肠癌组织,发现其低表达与p53降解加速相关,提示TP53INP1作为抑癌基因通过稳定p53抑制肿瘤进展。
3. **文献名称**:*Oxidative stress induces TP53INP1 nuclear localization via a p53-dependent pathway*
**作者**:Canepa et al.
**摘要**:研究采用TP53INP1抗体进行细胞核/质分离实验,证明氧化应激通过p53信号驱动TP53INP1核转位,进而增强DNA损伤修复能力。
4. **文献名称**:*TP53INP1 deficiency promotes liver cancer metastasis through EMT activation*
**作者**:Wang et al.
**摘要**:利用TP53INP1敲除小鼠模型及抗体检测(免疫印迹),发现TP53INP1缺失通过上皮-间质转化(EMT)促进肝癌转移,提示其临床预后价值。
注:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用时需核对原文信息及数据库更新情况。建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以关键词“TP53INP1 antibody”或“TP53INP1 immunohistochemistry”获取最新研究。
The TP53INP1 (Tumor Protein 53-Induced Nuclear Protein 1) antibody is a tool used to detect and study the TP53INP1 protein, which plays a critical role in cellular stress responses and tumor suppression. TP53INP1 is a p53-inducible gene that encodes a nuclear protein involved in regulating apoptosis, autophagy, and cell cycle arrest. It acts as a tumor suppressor by enhancing p53-mediated transcriptional activity and stabilizing p73. another member of the p53 family. Dysregulation of TP53INP1 has been linked to cancer progression, particularly in pancreatic, breast, and colorectal cancers, where its downregulation is associated with poor prognosis.
The TP53INP1 antibody is widely used in research to investigate protein expression patterns, subcellular localization (nuclear/cytoplasmic), and interactions in various biological contexts. It is essential for Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) applications, enabling the study of TP53INP1's role in oxidative stress, DNA damage responses, and autophagy pathways. Researchers also utilize this antibody to explore TP53INP1's dual isoforms (α and β) and their distinct functional roles.
Commercial TP53INP1 antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, targeting specific epitopes within the protein's conserved regions. Validation includes testing for specificity via knockout controls or siRNA-mediated silencing. Understanding TP53INP1 dynamics through these antibodies provides insights into cancer mechanisms, therapeutic resistance, and potential strategies to restore its tumor-suppressive functions in malignancies.
×