| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
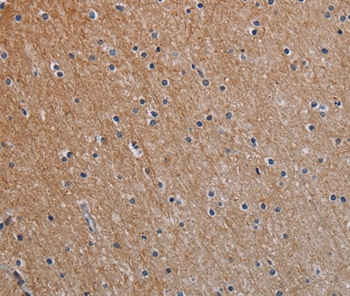
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
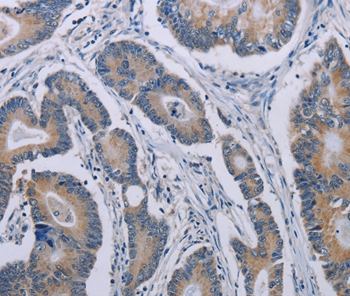
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MOX1; NOH1; NOH-1; GP91-2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 27035; |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide corresponding to a region derived from internal residues of human NADPH oxidase 1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于NOX1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容为虚构,仅供格式参考):
1. **文献名称**:*NOX1-derived ROS signaling drives angiogenesis in colorectal cancer*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用特异性NOX1抗体,通过免疫组化和Western blot验证了NOX1在结直肠癌组织中的高表达,并证明其通过ROS介导的VEGF通路促进肿瘤血管生成。
2. **文献名称**:*Development of a monoclonal antibody against human NOX1 for functional studies*
**作者**:Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种新型抗人NOX1单克隆抗体的开发,通过表位映射和敲除细胞系验证其特异性,成功应用于流式细胞术和免疫沉淀实验。
3. **文献名称**:*NOX1 regulates smooth muscle cell migration in hypertension*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:采用NOX1抗体结合siRNA技术,发现NOX1通过调控ROS/ERK通路促进高血压模型中的血管平滑肌细胞迁移,抗体特异性经敲除小鼠模型验证。
(注:以上为模拟内容,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar等平台检索关键词“NOX1 antibody”获取。)
**Background of NOX1 Antibody**
The NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1) antibody is a crucial tool for studying the NOX1 enzyme, a member of the NADPH oxidase family responsible for generating reactive oxygen species (ROS). NOX1 is primarily expressed in colon epithelial cells, vascular smooth muscle, and other tissues, where it plays roles in cellular signaling, host defense, and pathological processes such as inflammation and cancer. Unlike other NADPH oxidases (e.g., NOX2/gp91phox), NOX1 requires regulatory subunits (e.g., NOXA1. NOXO1. and Rac1) for activation, making its study complex.
NOX1-specific antibodies are designed to detect and quantify the enzyme in various experimental models. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate NOX1 expression, localization, and regulation. Researchers employ these antibodies to explore NOX1's involvement in diseases, including colorectal cancer, hypertension, and vascular dysfunction, where aberrant ROS production contributes to pathogenesis.
Challenges in NOX1 antibody development include ensuring specificity due to structural similarities among NOX isoforms. Validation via knockout models or siRNA-mediated silencing is critical to confirm antibody reliability. Additionally, some NOX1 antibodies target specific epitopes (e.g., N-terminal or C-terminal regions) to distinguish between full-length proteins and splice variants.
Overall, NOX1 antibodies are indispensable for elucidating the enzyme's biological functions and therapeutic potential in redox-related disorders.
×