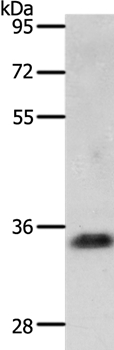
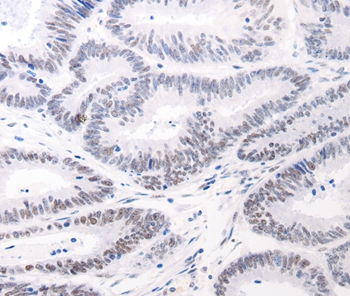
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AP-1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3727; |
| WB Predicted band size | 35kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide corresponding to a region derived from internal residues of human jun D proto-oncogene |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于JUND抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容的简要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*"JUND regulates pancreatic β cell survival during metabolic stress"*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用JUND特异性抗体通过染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)和Western blot技术,揭示了JUND在代谢应激条件下对胰岛β细胞存活的关键调控作用,表明其通过抑制氧化应激相关基因的表达维持细胞功能。
2. **文献名称**:*"JUND-mediated transcriptional control in cancer progression"*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化(IHC)和免疫荧光(IF)实验,研究者使用JUND抗体分析多种癌症样本,发现JUND表达水平与肿瘤侵袭性呈负相关,提示其可能通过抑制上皮-间质转化(EMT)路径发挥抑癌作用。
3. **文献名称**:*"The role of JUND in macrophage polarization and inflammation"*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用JUND抗体进行流式细胞术和共聚焦显微镜观察,证明JUND通过调控IL-10等抗炎因子表达促进M2型巨噬细胞极化,从而缓解实验性结肠炎模型中的炎症反应。
---
以上文献均涉及JUND抗体的具体实验应用(如Western blot、ChIP、IHC等),并围绕JUND在代谢、癌症和免疫中的功能展开。如需更多文献或补充DOI信息可进一步说明。
The JUND antibody is a crucial tool in molecular biology research for studying the JunD protein, a member of the AP-1 (Activator Protein 1) transcription factor family. JunD, encoded by the *JUND* gene, regulates gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences (AP-1 sites) in promoter or enhancer regions. It plays diverse roles in cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, stress response, and inflammation. Unlike other AP-1 subunits (e.g., c-Jun, c-Fos), JunD is often associated with both pro-survival and tumor-suppressive functions, depending on cellular context.
JUND antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, immunofluorescence, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to investigate JunD’s expression, localization, protein interactions, and DNA-binding activity. These antibodies are essential for understanding JunD’s involvement in diseases such as cancer, immune disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions. Researchers rely on validated JUND antibodies to ensure specificity, as cross-reactivity with other AP-1 family members (e.g., c-Jun, JunB) can lead to inaccurate results.
Commercial JUND antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, with monoclonal and polyclonal variants available. Proper validation via knockout cell lines or siRNA knockdown is critical to confirm antibody reliability. The choice of antibody depends on experimental needs, including species reactivity (human, mouse, rat), application compatibility, and epitope-targeted regions (N-terminal, C-terminal, or full-length JunD).
×