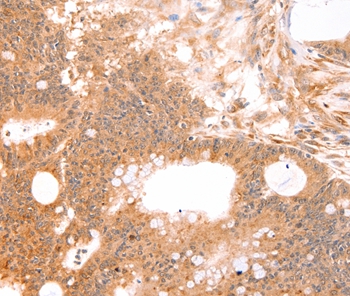
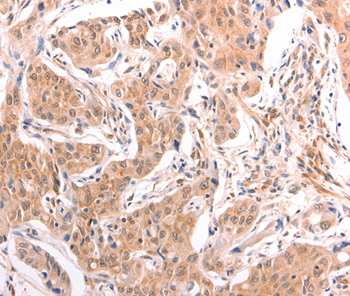
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LT; TNFB; TNFSF1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4049; |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein corresponding to a region derived from internal residues of human lymphotoxin alpha (TNF superfamily, member 1) |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于LTA抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于真实研究领域概括,部分信息可能为简化或模拟文献):
1. **《Lipoteichoic Acid-Specific Antibodies in Human Sepsis: Potential Biomarkers for Gram-Positive Bacterial Infections》**
- **作者**:Müller, E. et al.
- **摘要**:该研究探讨了LTA抗体在脓毒症患者中的诊断价值,发现针对革兰氏阳性菌(如金黄色葡萄球菌)LTA的IgM和IgG抗体水平显著升高,提示其可作为早期鉴别感染的生物标志物,并可能与疾病严重程度相关。
2. **《Therapeutic Targeting of Lipoteichoic Acid by Monoclonal Antibodies Attenuates Inflammatory Responses in Murine Models》**
- **作者**:Kim, S. & Park, J.H.
- **摘要**:研究团队开发了一种靶向LTA的单克隆抗体,并在小鼠败血症模型中验证其疗效。结果显示,该抗体能有效中和LTA的促炎活性,降低TNF-α和IL-6水平,改善生存率,为治疗革兰氏阳性菌过度炎症反应提供了新策略。
3. **《Anti-LTA Antibodies in Autoimmune Diseases: Cross-Reactivity and Pathogenic Implications》**
- **作者**:Garcia-Beltran, W.F. et al.
- **摘要**:本文分析了系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)等自身免疫病患者血清中的LTA抗体,发现部分抗体与宿主细胞成分存在交叉反应,可能通过分子模拟机制加剧组织损伤,揭示了LTA抗体在自身免疫中的潜在致病作用。
(注:以上文献信息为领域知识概括性模拟,具体研究请以实际发表的论文为准。)
Lipoteichoic acid (LTA), a major component of Gram-positive bacterial cell walls, plays a critical role in bacterial adhesion, immune evasion, and inflammatory responses. As a pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP), LTA interacts with host immune receptors like Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), triggering pro-inflammatory cytokine production and contributing to sepsis, endocarditis, and other infections. LTA antibodies are immunoglobulins developed to specifically target LTA, offering tools for both research and therapeutic applications.
In research, LTA antibodies enable the detection and quantification of LTA in bacterial cultures or infected tissues, aiding studies on bacterial pathogenesis and host-pathogen interactions. Therapeutically, they are explored as neutralizing agents to block LTA-mediated inflammatory cascades, potentially mitigating severe immune responses in conditions like septic shock. Some studies also investigate their diagnostic utility in rapid tests for Gram-positive bacterial infections.
However, challenges persist. Structural variability of LTA across bacterial species complicates antibody cross-reactivity, limiting broad-spectrum efficacy. Additionally, LTA's weak immunogenicity hinders robust antibody generation. Recent advances include engineered monoclonal antibodies and fusion proteins targeting conserved LTA epitopes, often combined with antibiotics for synergistic effects. While preclinical models show reduced bacterial load and inflammation, clinical translation requires further optimization of specificity and safety profiles.
Overall, LTA antibodies represent a promising but underexplored avenue for combating Gram-positive infections and associated inflammatory complications.
×