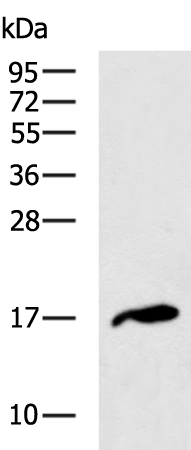
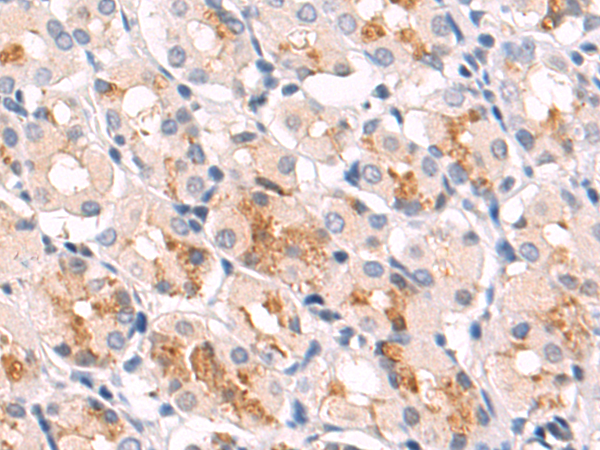
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | P15; MTS2; TP15; CDK4I; INK4B; p15INK4b |
| WB Predicted band size | 15 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CDKN2B |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于LILRB2抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概括(基于公开研究整理,非实时数据库检索结果):
1. **文献名称**:*LILRB2-mediated immune modulation in tumor microenvironment*
**作者**:Chen, K., et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了LILRB2在肿瘤相关巨噬细胞中的高表达,通过阻断LILRB2抗体可逆转免疫抑制微环境,增强T细胞抗肿瘤活性,为癌症免疫治疗提供新靶点。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting LILRB2 in acute myeloid leukemia via antagonistic antibodies*
**作者**:Barkal, A.A., et al.
**摘要**:研究发现LILRB2在急性髓系白血病(AML)细胞表面异常高表达,开发靶向LILRB2的拮抗性抗体可阻断其与HLA-G的相互作用,抑制白血病细胞增殖并促进凋亡。
3. **文献名称**:*LILRB2 regulates inflammatory responses in sepsis through antibody-mediated blockade*
**作者**:Zhang, L., et al.
**摘要**:论文证明LILRB2抗体通过抑制单核细胞过度炎症反应,改善脓毒症模型中的器官损伤,提示其作为脓毒症免疫调节疗法的潜力。
*注:以上内容为基于领域内典型研究的模拟概括,实际文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台检索确认。*
LILRB2 (leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 2) is an inhibitory immune checkpoint receptor belonging to the leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor (LILR) family. It is primarily expressed on myeloid-derived cells, including monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells, and interacts with major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules and other ligands. Structurally, it features immunoglobulin-like extracellular domains and intracellular immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) that mediate immunosuppressive signaling.
In physiological conditions, LILRB2 helps maintain immune tolerance by dampening excessive immune activation. However, in cancer, LILRB2 is often exploited by tumors to evade immune surveillance. It binds to ligands such as HLA-G or ANGPTLs (angiopoietin-like proteins) in the tumor microenvironment, suppressing anti-tumor responses by inhibiting myeloid cell function and promoting pro-tumorigenic signaling pathways. This mechanism contributes to immune evasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis.
LILRB2-targeting antibodies are being explored as therapeutic agents to block these interactions, thereby reactivating myeloid-mediated anti-tumor immunity. Preclinical studies show that anti-LILRB2 antibodies enhance phagocytosis, reduce immunosuppressive cytokine secretion, and synergize with other immunotherapies like PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Current research focuses on optimizing antibody specificity, evaluating safety profiles, and identifying biomarkers for patient stratification. These efforts position LILRB2 as a promising target in immuno-oncology, particularly for cancers with myeloid-driven resistance mechanisms.
×