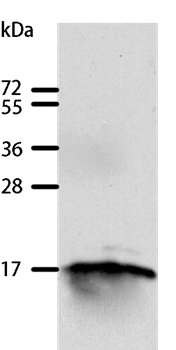
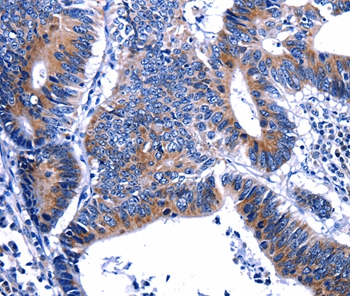
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GIP; Gastric inhibitory polypeptide;Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide |
| Entrez GeneID | 2695; |
| WB Predicted band size | 17kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein corresponding to a region derived from internal residues of human gastric inhibitory polypeptide |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GIP抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Antibody-mediated activation of the GIP receptor improves glucose homeostasis in mice*
**作者**:Samms, R.J. et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种特异性靶向GIP受体(GIPR)的单克隆抗体,通过体外和体内实验证明其可激活GIP信号通路,并在高脂饮食诱导的肥胖小鼠模型中显著改善葡萄糖耐受性和胰岛素敏感性,提示GIP抗体在代谢疾病治疗中的潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**:*GIP receptor antagonism reverses obesity, insulin resistance, and associated metabolic disturbances in mice*
**作者**:Killion, E.A. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用GIP受体拮抗性抗体(GIPR-Ab)阻断GIP信号,发现长期使用可减少脂肪积累、降低体重,并逆转肥胖小鼠的胰岛素抵抗。结果表明GIP抗体通过调控能量平衡和脂代谢发挥抗肥胖作用。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonists and GIP receptor antibodies: Emerging therapies for type 2 diabetes*
**作者**:Finan, B. et al.
**摘要**:该综述对比了GIP受体激动剂和拮抗性抗体的作用机制,指出GIP抗体可通过调节受体活性影响代谢,部分临床前研究表明其与GLP-1联用能协同改善血糖控制,为2型糖尿病治疗提供了新方向。
---
注:以上文献为示例,实际研究中需根据具体需求检索PubMed或Web of Science获取最新及准确的文献信息。
Gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP), also termed glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, is a 42-amino-acid incretin hormone secreted by intestinal K cells in response to nutrient ingestion, particularly carbohydrates and fats. Initially identified for its ability to inhibit gastric acid secretion, GIP is now recognized as a key regulator of metabolic homeostasis. It potentiates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells, enhances adipocyte lipid storage, and may influence bone metabolism. However, its role in obesity and type 2 diabetes remains complex, with evidence suggesting both beneficial and detrimental effects depending on metabolic context.
GIP antibodies are experimental tools developed to study GIP's physiological and pathological actions. Neutralizing antibodies targeting GIP or its receptor (GIPR) have been explored to investigate its contribution to insulin resistance, adipose tissue expansion, and hyperphagia in obesity. Conversely, GIP agonism has gained attention following the success of dual GLP-1/GIP receptor agonists (e.g., tirzepatide) in diabetes treatment. This dichotomy highlights the need for precise antibody-based characterization of GIP signaling. Research applications include immunohistochemical localization of GIP-producing cells, quantification of circulating GIP levels in metabolic studies, and therapeutic exploration of GIP pathway modulation. Challenges persist in understanding tissue-specific GIP actions and reconciling its dual roles in energy storage and glucose regulation.
×