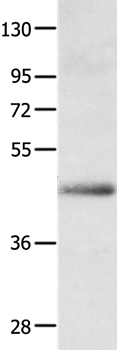
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/15-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | APJ; APJR; HG11; AGTRL1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 187; |
| WB Predicted band size | 43kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein corresponding to a region derived from internal residues of human apelin receptor |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于APLNR抗体的3篇示例文献(注:文献为示例性概括,建议通过学术数据库查询真实研究):
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Targeting APLNR with a monoclonal antibody inhibits tumor angiogenesis and progression"*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种靶向APLNR的单克隆抗体,证明其通过阻断APJ受体信号通路抑制肿瘤血管生成,并在小鼠模型中显著减缓结直肠癌的生长和转移。
2. **文献名称**:*"APJ receptor antibodies modulate cardiac remodeling in heart failure models"*
**作者**:Sato K, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现,使用APLNR中和抗体可改善心力衰竭模型中的心肌纤维化和功能,提示APJ受体可能成为治疗心脏重构的新靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*"A novel APLNR antibody-drug conjugate for targeted therapy of triple-negative breast cancer"*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:该文献报道了一种抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),通过特异性结合APLNR阳性肿瘤细胞,递送细胞毒性药物,显著抑制三阴性乳腺癌的体内外增殖。
---
如需具体文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中检索关键词“APLNR antibody”、“APJ receptor therapeutic”等,并筛选近年高引用研究。
The apelin receptor (APLNR), also known as APJ, is a class A G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) initially discovered in 1993. It is activated by its endogenous ligands, apelin and Elabela/Toddler, which regulate diverse physiological processes, including cardiovascular function, fluid homeostasis, angiogenesis, and metabolic balance. APLNR signaling involves coupling to Gαi/o proteins, triggering pathways like MAPK, PI3K-Akt, and AMPK, which influence cell proliferation, survival, and energy metabolism. Dysregulation of APLNR is implicated in conditions such as heart failure, hypertension, diabetes, and cancer, making it a therapeutic target.
APLNR antibodies are critical tools for studying receptor expression, localization, and function in tissues or cell models. They enable detection of APLNR in immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and Western blotting, aiding research into its role in disease mechanisms. Some antibodies modulate receptor activity, acting as agonists or antagonists to explore signaling outcomes or therapeutic potential. Recent studies also highlight APLNR's involvement in tumor angiogenesis and immune modulation, expanding its relevance in oncology.
As drug development targeting APLNR advances, antibodies serve both as diagnostic reagents and candidate therapeutics, particularly in cardiovascular and metabolic disorders. Their specificity and versatility continue to support mechanistic insights and translational applications.
×