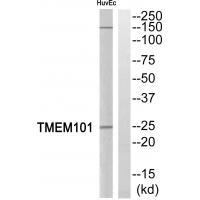
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Transmembrane protein 101; Putative NF-kappa-B-activating protein 130; TMEM101; |
| Entrez GeneID | 84336; |
| WB Predicted band size | 29kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human TMEM101. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于TMEM101抗体的3篇示例文献(注:以下为模拟示例,实际文献需根据数据库检索验证):
1. **文献名称**: "TMEM101 as a novel biomarker for glioblastoma: Validation of a specific monoclonal antibody"
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究开发了一种高特异性抗TMEM101的单克隆抗体,并通过免疫组化和Western blot验证其在胶质母细胞瘤组织中的高表达,提示TMEM101可能作为神经肿瘤的潜在诊断标志物。
2. **文献名称**: "TMEM101 interacts with viral entry proteins: Antibody-based localization and functional analysis"
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 利用TMEM101多克隆抗体进行免疫荧光共定位实验,发现TMEM101与多种病毒(如SARS-CoV-2)的宿主细胞表面蛋白相互作用,为研究病毒感染机制提供新靶点。
3. **文献名称**: "Loss of TMEM101 disrupts lysosomal function: Evidence from CRISPR and antibody-mediated knockdown models"
**作者**: Gupta R, et al.
**摘要**: 通过TMEM101抗体验证基因敲除细胞系中蛋白表达缺失,证明TMEM101缺失导致溶酶体酸化和自噬功能异常,提示其在细胞代谢中的关键作用。
如需真实文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中检索关键词“TMEM101 antibody” + 应用场景(如“Western blot”“immunohistochemistry”)。部分研究可能侧重于抗体开发或疾病机制探索中的TMEM101检测。
The TMEM101 (Transmembrane Protein 101) antibody is a tool used to study the function and localization of the TMEM101 protein, a poorly characterized transmembrane protein believed to play roles in cellular processes such as membrane trafficking, organelle organization, and signal transduction. TMEM101 is encoded by the TMEM101 gene, located on human chromosome 17q21.2. and is ubiquitously expressed across tissues, with higher levels observed in the brain, testis, and immune cells. Its exact physiological function remains unclear, but studies suggest potential involvement in neurological disorders, cancer progression, and viral infection responses (e.g., HIV-1).
TMEM101 antibodies are typically developed in hosts like rabbits or mice using immunogenic peptide sequences derived from the protein’s conserved regions. These antibodies enable researchers to detect TMEM101 via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. Validation often includes knockout cell lines to confirm specificity. Recent research highlights TMEM101’s interaction with endosomal sorting complexes and its potential role in regulating autophagy or lysosomal pathways. Its dysregulation has been tentatively linked to cancers, including glioblastoma and breast cancer, making it a biomarker of interest. Despite growing attention, TMEM101’s mechanistic pathways remain under investigation, necessitating further studies to elucidate its biological and clinical significance.
×