| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
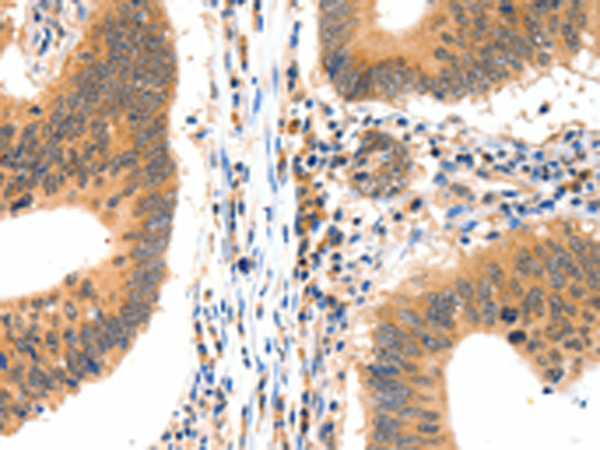
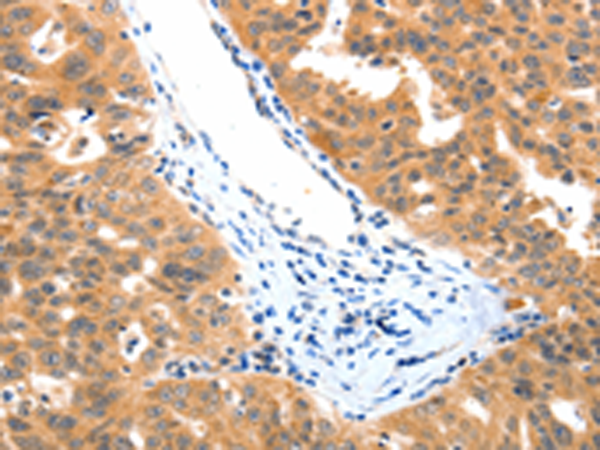
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LSFC, GP130, LRP130, CLONE-23970 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human LRPPRC |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与FGF13抗体相关的文献摘要概括,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**:*FGF13 regulates hippocampal neuronal excitability and cognitive functions via modulation of sodium channel gating*
**作者**:Wang Y. et al. (2020)
**摘要**:本研究利用FGF13特异性抗体进行免疫印迹和免疫组化,发现FGF13通过调控电压门控钠通道(Nav1.6)的活性影响海马神经元兴奋性。基因敲除小鼠模型显示FGF13缺失导致认知功能障碍,抗体实验验证了其在中枢神经系统的定位与表达。
---
2. **文献名称**:*FGF13 deficiency leads to X-linked recessive developmental epileptic encephalopathy in humans*
**作者**:Al-Mehmadi S. et al. (2019)
**摘要**:通过患者基因测序结合FGF13抗体免疫荧光分析,发现FGF13基因突变导致神经元迁移异常和癫痫性脑病。抗体标记显示突变体FGF13蛋白稳定性下降,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点的价值。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Antibody-based profiling of FGF13 isoforms reveals distinct roles in colorectal cancer progression*
**作者**:Chen L. et al. (2021)
**摘要**:开发了针对FGF13不同亚型的特异性抗体,发现FGF13V(胞质亚型)在结直肠癌中高表达并与转移相关。抗体阻断实验表明其通过Wnt/β-catenin通路促进肿瘤侵袭,为癌症生物标志物研究提供新方向。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索最新论文,并核对抗体应用的具体实验方法(如克隆号、物种来源等)。
Fibroblast Growth Factor 13 (FGF13) is a member of the FGF family, which primarily functions in cellular signaling, development, and repair. Unlike canonical FGFs, FGF13 lacks a secretory signal peptide and acts intracellularly, modulating ion channels and cytoskeletal dynamics rather than binding FGF receptors. It is particularly critical in nervous system development, where it stabilizes microtubules to support neuronal migration, axon guidance, and synaptic plasticity. FGF13 also interacts with voltage-gated sodium channels (Navs) to regulate electrical activity in neurons and cardiomyocytes. Genetic mutations in FGF13 are linked to X-linked developmental disorders, including intellectual disability, epilepsy, and congenital heart defects, underscoring its physiological importance.
FGF13 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and functional roles. They enable detection of FGF13 isoforms (e.g., FGF13A, FGF13B) via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Researchers use these antibodies to explore FGF13's involvement in neurodevelopmental disorders, cardiac arrhythmias, and cancer, where aberrant FGF13 expression correlates with tumor progression. Additionally, FGF13 antibodies aid in dissecting molecular mechanisms, such as its interplay with Nav channels or microtubule-associated proteins. Validating antibody specificity is crucial due to FGF13's homology with other FGFs and splice variants. These reagents hold potential for diagnostic applications and targeted therapies in FGF13-related pathologies.
×