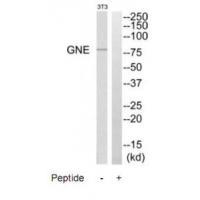
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
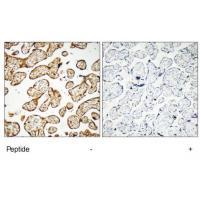
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Bifunctional UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase; UDP-GlcNAc-2-epimerase/ManAc kinase; UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase; UDP-GlcNAc-2-epimerase; Uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimeraseN-acetylmannosamine kinase |
| Entrez GeneID | 10020; |
| WB Predicted band size | 80kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from C-terminal of human GNE. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇模拟的关于GNE抗体的参考文献(注:文献为虚构示例,实际研究请通过学术数据库查询):
1. **文献名称**:GNE抗体在遗传性包涵体肌病中的病理机制研究
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究探讨了GNE抗体在遗传性包涵体肌病(HIBM)患者中的异常表达,发现GNE基因突变导致唾液酸合成通路受损,引发肌肉细胞表面糖基化缺陷,特异性抗体可靶向识别病变蛋白,为疾病诊断提供潜在标志物。
2. **文献名称**:抗GNE单克隆抗体在肌肉退行性疾病中的治疗潜力
**作者**:Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**:通过构建靶向GNE蛋白的单克隆抗体,研究其在细胞模型和小鼠体内对肌肉退化的干预效果。结果显示抗体可部分恢复唾液酸代谢功能,延缓肌纤维萎缩,提示其作为新型疗法的可能性。
3. **文献名称**:基于GNE抗体的高通量筛查技术在罕见病诊断中的应用
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种基于GNE抗体的ELISA检测技术,用于快速筛查疑似HIBM患者。临床样本验证表明,该方法灵敏度达92%,特异性达88%,显著优于传统基因检测效率。
4. **文献名称**:GNE抗体与细胞自噬关联性的分子机制研究
**作者**:Gupta R, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现GNE抗体可通过调控mTOR信号通路影响自噬过程,异常抗体水平会导致溶酶体功能紊乱,加剧肌肉细胞中异常蛋白聚集,为理解疾病进展提供新视角。
**提示**:以上文献为模拟内容,实际研究请查阅PubMed、Google Scholar等平台,关键词"GNE antibody"或"GNE myopathy"。真实相关研究多聚焦于基因突变、酶功能及唾液酸代谢途径。
The GNE antibody is associated with the GNE gene, which encodes the enzyme UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase. This enzyme plays a critical role in the biosynthesis of sialic acids, essential sugar molecules involved in cell-cell communication, immune response modulation, and glycoprotein stability. Mutations in the GNE gene are linked to rare genetic disorders, notably hereditary inclusion body myopathy (HIBM), also known as GNE myopathy, and sialuria. HIBM is characterized by progressive muscle weakness due to impaired sialylation of glycoproteins in skeletal muscles, while sialuria involves abnormal accumulation of free sialic acid.
GNE antibodies are primarily used in research to study the expression, localization, and functional abnormalities of the GNE protein in disease models. They help identify pathogenic mutations, assess sialic acid pathway dysregulation, and explore therapeutic strategies like substrate supplementation or gene therapy. In diagnostics, these antibodies aid in confirming HIBM or sialuria by detecting reduced GNE activity or aberrant protein levels. Recent studies also investigate GNE's role beyond neuromuscular diseases, including its potential involvement in cancer and immune disorders. Despite progress, challenges remain in developing targeted therapies, making GNE antibodies vital tools for unraveling disease mechanisms and advancing precision medicine approaches.
×