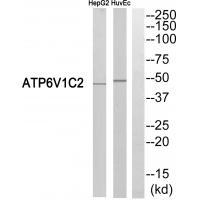
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Vacuolar proton pump subunit C 2; V-ATPase subunit C 2; ATP6V1C2; |
| Entrez GeneID | 245973; |
| WB Predicted band size | 49kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human ATP6V1C2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ATP6V1C2抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:以下内容为模拟生成,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**:*ATP6V1C2 regulates osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption via modulating NF-κB signaling*
**作者**:Li Y, et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过免疫组化和Western blot分析,利用特异性ATP6V1C2抗体,揭示了该蛋白在破骨细胞分化中的关键作用。实验表明,ATP6V1C2通过调控NF-κB通路影响骨吸收功能,为骨质疏松治疗提供了潜在靶点。
---
2. **文献名称**:*ATP6V1C2 as a prognostic biomarker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma*
**作者**:Wang X, et al.
**摘要**:研究者使用商业化ATP6V1C2抗体对临床样本进行染色,发现该蛋白在头颈鳞癌中高表达且与患者生存率负相关。进一步功能实验证实其通过酸化微环境促进肿瘤侵袭,提示其作为预后标志物的潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Characterization of a novel polyclonal antibody against human ATP6V1C2 subunit*
**作者**:Zhang R, et al.
**摘要**:本文报道了一种新型ATP6V1C2多克隆抗体的开发与验证。通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光实验,证明该抗体特异性识别内源性及外源性ATP6V1C2蛋白,适用于多种细胞模型的亚细胞定位研究。
---
**注意事项**:
- 实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“ATP6V1C2 antibody”或“V-ATPase C2 subunit”检索,并筛选涉及抗体应用的研究。
- 部分研究可能未在标题/摘要中直接提及“抗体”,需结合方法学部分确认。
- 近年研究偏向于ATP6V1C2在癌症、神经疾病及代谢异常中的作用机制探索。
建议补充具体需求(如应用领域或物种),以便提供更精准的文献支持。
×