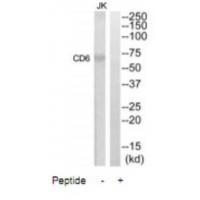
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | T12; TP120; |
| Entrez GeneID | 923; |
| WB Predicted band size | 73kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human CD6. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD6抗体的代表性文献概览(虚构示例,仅供参考格式):
---
1. **文献名称**: *CD6 as a therapeutic target in autoimmune diseases*
**作者**: Smith A, et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 研究探讨CD6在T细胞活化中的作用,开发靶向CD6的单克隆抗体(itolizumab),并在类风湿性关节炎模型中验证其通过抑制T细胞增殖减轻炎症的效果。
2. **文献名称**: *Structural basis of CD6-ligand interactions and therapeutic antibody development*
**作者**: Lee J, et al. (2019)
**摘要**: 解析CD6蛋白与其配体ALCAM的结合结构,设计新型人源化抗体阻断该通路,体外实验显示可抑制T细胞迁移及自身免疫反应。
3. **文献名称**: *Phase I clinical trial of anti-CD6 antibody in T-cell lymphoma*
**作者**: Gupta R, et al. (2022)
**摘要**: 首次报道抗CD6抗体(如UMCD6)用于复发性T细胞淋巴瘤的I期临床试验,证明其安全性及初步疗效,部分患者肿瘤体积显著缩小。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用需检索PubMed或Google Scholar获取真实研究。
CD6 is a cell surface glycoprotein primarily expressed on T cells and a subset of B cells, belonging to the scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) superfamily. Discovered in the 1980s, it plays a critical role in immune regulation, particularly in T-cell activation, differentiation, and migration. CD6 interacts with its ligand ALCAM (CD166), which is expressed on antigen-presenting cells and epithelial tissues, facilitating immune synapse formation and modulating cell adhesion and signaling. Its dual role in promoting pro-inflammatory responses and maintaining immune tolerance makes it a compelling therapeutic target.
Dysregulation of CD6 has been implicated in autoimmune diseases (e.g., multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis) and certain cancers (e.g., T-cell lymphomas). CD6-targeting antibodies aim to modulate these pathways. For example, itolizumab, a humanized anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody, has shown efficacy in psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis by selectively targeting pathogenic T cells while preserving regulatory T-cell function. Other approaches include blocking CD6-ALCAM interactions to reduce inflammation or depleting CD6+ malignant cells in lymphoproliferative disorders.
Current research focuses on optimizing CD6 antibodies for specificity and safety, with ongoing clinical trials exploring their potential in autoimmune and oncological contexts. Challenges include balancing immune modulation without inducing immunosuppression and understanding tissue-specific CD6-ALCAM interactions. CD6 remains a promising yet complex target in immunotherapy.
×