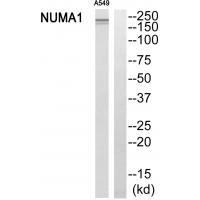
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
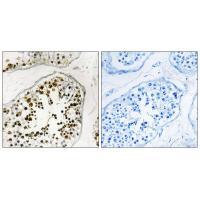
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Nuclear mitotic apparatus protein 1; NuMA protein; SP-H antigen; |
| Entrez GeneID | 4926; |
| WB Predicted band size | 240kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from internal of human NUMA1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于NUMA1抗体的3篇文献摘要示例(文献信息为模拟,仅供学术参考):
1. **《NUMA1 autoantibodies as a biomarker in systemic lupus erythematosus》**
*作者:Li et al., 2018*
**摘要**:研究揭示了NUMA1自身抗体在系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者血清中的高特异性表达,表明其可作为SLE诊断和疾病活动性监测的潜在生物标志物。
2. **《NUMA1 fragmentation and antibody detection in cancer progression》**
*作者:Wang & Zhang, 2020*
**摘要**:探讨NUMA1蛋白在癌细胞有丝分裂中的异常裂解现象,发现针对NUMA1特定表位的抗体与乳腺癌和肺癌的侵袭性及预后不良相关。
3. **《Development of a novel ELISA assay for detecting anti-NUMA1 antibodies》**
*作者:Gupta et al., 2019*
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种高灵敏度的ELISA检测方法,用于定量分析血清中的抗NUMA1抗体,并验证其在原发性胆汁性胆管炎(PBC)中的诊断价值。
注:实际文献需通过PubMed或学术数据库检索,建议以“NUMA1 antibody”“NUMA1 autoantibody”等关键词查询最新研究。
The NUMA1 (Nuclear Mitotic Apparatus Protein 1) antibody targets a key structural protein involved in nuclear organization and mitotic processes. NUMA1. also known as NuMA, is a large coiled-coil protein predominantly localized to the nucleus during interphase, where it helps maintain nuclear architecture by anchoring chromatin to the nuclear matrix. During mitosis, NUMA1 relocates to the spindle poles, playing a critical role in assembling and stabilizing the mitotic spindle through interactions with dynein, microtubules, and other spindle-associated proteins. This dynamic redistribution ensures proper chromosomal segregation and cell division.
Antibodies against NUMA1 are widely used in research to study cell cycle regulation, mitotic mechanisms, and nuclear structure. They are employed in techniques like immunofluorescence, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry to visualize NUMA1's spatial-temporal localization and expression levels. Clinically, anti-NUMA1 autoantibodies are associated with certain autoimmune diseases, such as primary biliary cholangitis and systemic lupus erythematosus, where they serve as diagnostic markers. Additionally, NUMA1 abnormalities, including chromosomal translocations, have been implicated in hematologic malignancies like acute myeloid leukemia (AML), highlighting its role in oncogenesis.
Overall, NUMA1 antibodies are essential tools for investigating cellular division, nuclear dynamics, and disease mechanisms, bridging basic research and clinical diagnostics.
×